Westward Expansion & The Gilded Age
- 1. Westward Expansion Section 1 of 2
- 2. The Great Plains Native Americans disrupted expansionist dreams of white settlers in the east for decades During the 1860s Indian tribes on the Great Plains began disrupting dreams of Manifest Destiny As president, Andrew Jackson moved the Cherokees from the SE along the Trail of Tears to reservations in present-Oklahoma This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 3. The Great Plains...Cont’d. Perhaps Jackson didn’t think America would stretch across the plains He didn’t address the situation of the Natives roaming free around the Great Plains Geographically, the Great Plains stretch from North Dakota to Eastern New Mexico This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 4. The Great Plains...Cont’d. Scientists believe the plains formed 60 million years before 1860 The Rockies rose out of the sea, caused the shallow sea to the east to dry up Left a bare surface Little vegetation Only roaming animals (grazing) survived well This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 5. Tribes of the Great Plains The Sioux are a great example of tribes on the plains Originally from northern Minnesota area Crossed MO River in 1760 Nomadic people—followed the buffalo Acquired horses from SW tribes/became skilled riders and warriors This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 6. Tribes of the Great Plains...Cont’d. Claimed the entire plains north of Arkansas River as hunting grounds Religion was polytheistic=many gods Traded w/French trappers for kettles, blankets, knives, and firearms This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 7. The “Great American Desert” Americans first thought the Great Plains were better off with the Indians Agriculturally, Americans thought the land was worth little When gold was discovered in California (1840s) Americans wanted a quicker way west 12,000 wagons traveled to Oregon and California This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 8. The “Great American Desert”...Cont’d. Missouri was called the “Gateway to the West” It was the last “civilization” before the plains The 1 st wagon train of white travelers left Missouri in 1842 Travelers faced natives, little food, vicious weather, tight conditions This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 9. The Railroad After the US gained territory from Mexico (1848) the Trans-Continental RR was built The route west was through Indian country, very few towns and little white population The Government spent a lot of $ building the lines This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 11. The Railroad...Cont’d. Union Pacific built from Nebraska Central Pacific built from further east Met at Promontory Point, Utah in 1869 During the 1880s, 40,000 miles of track were laid linking California to New Orleans and Kansas City to Minnesota Nearly 5 million longhorn cattle grazed on Texas ranches This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 12. The Railroad...Cont’d. It was unprofitable to drive them north By 1865 the Missouri Pacific RR reached Sedalia If ranchers got cattle to Sedalia the cars would move them west Cattle was worth $40 in the north and $5 in Texas This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 13. The Homesteaders To convince Americans to move west the US government passed the Homestead Act (1862) Granted 160 acres of land to settlers in Kansas An attempt to move settlers west Moving west was a major decision Caused gender shifts This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 14. The Homesteaders...Cont’d. Gender Role -the tasks (jobs), attitudes & actions society believes a man or women should complete or possess Women were to cook, clean and raise children Men were for manual labor, providing and “thinking” for the family Women worked alongside men on the plains This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 15. The Indian Wars The Trans-Continental Railroad spread across the plains Ranchers’ lands grew Homesteaders settled the plains Gold was still dug in California Indians faced extinction This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 16. The Indian Wars...Cont’d. Sioux Chief Red Cloud said in 1870: “ The white children have surrounded me and left me nothing but an island…When we first had all this land we were strong; now we are all melting like snow on a hillside, while you [white Americans] are grown like spring grass.” By the 1870s most Americans agreed Indians should be moved off the plains or concentrated somewhere This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
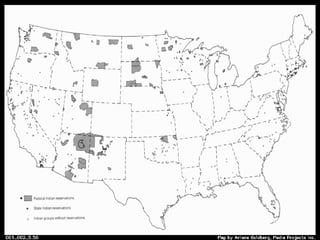
- 17. The Reservations Reservations required assimilation to white culture Assimilation -taking on the attitudes, appearance, and sensibilities of another culture South Dakota—Sioux Oklahoma—Plains tribes and Choctaws, Cherokees, Chickasaws, Creeks, and Seminoles Southwest—Apaches, Navahos, Utes This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 19. The Reservations…Cont’d. Many tribes refused to move onto reservations Chief Joseph (Nez Perce) Marched his people 1,500 miles from Oregon to Canada Apaches fought w/Geronimo in New Mexico Tribes also fought throughout Kansas, Oklahoma, and Texas This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 20. Little Big Horn In 1868, a treaty was made between Sioux and the US government Sioux would always own Powder River hunting grounds In 1875, US government ordered Sioux to vacate Powder River and move to reservations Chief Sitting Bull led Sioux and Cheyenne warriors to the Little Big Horn River, west of the hunting grounds This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 21. Little Big Horn…Cont’d. The US military wanted to force the tribes back to the reservation George Custer led the assault of US Cavalry He did not know that the Indian warriors outnumbered him w/3 times his strength He divided his cavalry into 3 columns each being driven back This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 22. Little Big Horn…Cont’d. Custer faced one of the fiercest Sioux—Crazy Horse Custer ordered his men to shoot their horses to make a wall Custer and his men were killed before the Indians retreated from approaching reinforcements This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 23. Wounded Knee 1891 In response to the outlawing of native freedom (by the move to reservations) many natives looked to the shaman Wovoka Wovoka promised the “Ghost Dance” would bring back dead natives, buffalo would return, new soil would cover the whites and restore the prairie This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 24. Wounded Knee 1891…Cont’d. The Ghost Dance spread to Sioux reservations at Pine Ridge (SD) Scared white Indian Agents who called for protection Sitting Bull was killed in Canada in December This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 25. Wounded Knee 1891…Cont’d. Chief Big Foot was a target and led his people to the Pine Ridge Reservation They camped by Wounded Knee Creek While Bigfoot was meeting with the US officers someone fired a shot This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 26. Wounded Knee 1891…Cont’d. The natives scattered as the military poured gunfire into men, women, and children 25 US soldiers were dead compared with 300 Sioux The massacre at Wounded Knee ended the Ghost Dance movement and, for the most part, the Indian Wars This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 27. The gilded Age Section 2 of 2
- 28. The “Gilded Age” The Gilded Age followed Reconstruction Lasted from 1877-1900 Given the name by Missouri author, Mark Twain Gilded Age -Society was corrupt and gilded to cover its impurities and imperfections Characterized by three qualities: Excess , Greed , and Classism This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 29. What’s So Bad About Excess? The Credit Mobilier Scandal (1872) A director of the Union Pacific RR created a company (Credit Mobilier) to receive all government building contracts Paid $94 mil by Congress Only used $44 mil worth Sold shares to D.C. movers for half price This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 30. What’s So Bad About Excess?...Cont’d. Central Pacific RR Also created companies to gain government monies Benefited Leland Stanford of California Used the money to establish his famous Univesity This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 31. What’s So Bad About Excess?...Cont’d. Whiskey Ring Scandal US Treasury Dept. and President US Grant’s personal secretary defrauded the government Millions in taxes Represented what was to come This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 32. Robber Barons Robber Barons -American businessmen who made their fortunes from the expanding railroads Term coined in 1878 at the height of the railroad boom Three American capitalists especially earned the name: “Robber Baron” J.P. Morgan Sr., John D. Rockefeller, & Andrew Carnegie This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 33. J.P. Morgan Sr. Drafted into Union army after Gettysburg (Paid $300 for a filler) Purchased obsolete carbine rifles for $3.50/piece Sold them to a buyer for $11.00/piece Resold them back to the government for $22.00/piece This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 34. J.P. Morgan Sr....Cont’d. When gold prices fluctuated during the CW, he tried to rig the system by shipping gold out of the country He was a millionaire banker His banking house loaned money to countless banks By 1900 he owned half of America’s RR track mileage (His friends owned the rest) This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 35. John D. Rockefeller Began an oil operation in Ohio in mid-1860s Expanded to form Standard Oil in 1870 He didn’t have a monopoly... Other smaller oil companies existed Received rebates from the RR (lower shipping costs=higher profit) Also made secret payments and allowed price-cutting This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 36. John D. Rockefeller...Cont’d. Controlled 90% of nation’s oil-producing capacity by end of 1870s Government got involved (feared a monopoly) Standard Oil of Ohio could not legally own stock in other oil companies (or conduct business in other states) Standard Oil became a trust Trust -Caretakers (trustees) manage the money (because they have more power than the corp.) and spread holdings (because of no restrictions on trusts, only corporations) This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 37. Andrew Carnegie Immigrant from Scotland Went from telegraph clerk to private secretary of president of Pennsylvania RR Played the Stock Market throughout the 1860s—focused on steel in 1873 Revolutionized the manufacture of steel This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 38. Andrew Carnegie...Cont’d. Two main ideas: 1. Cut costs (increase profit) & 2. Vertical integration (control every step in production) Profit went into new equipment and the business Controlled mines (raw materials), boats (to move ore on rivers), RR (to move to mill), and a sales force (to market goods) This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 39. Consumer to Capital The Gilded Age was characterized by: Excess Greed Classism These three qualities revolved around one of the main features of the period: economic success This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 40. Consumer to Capital...Cont’d. Before the Gilded Age, American industry produced consumer goods Consumer Goods —goods directly related to agriculture & sold for consumer use During and after the Gilded Age, industry produced capital goods Capital Goods —goods that added to productive capacity of the economy This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 41. Consumer to Capital...Cont’d. Examples: Consumer Goods—textiles, shoes, paper, furniture Capital Goods—railroad track, machinery, construction material (steel) American industry relied on vertical integration and innovation Embodied in G.F. Swift This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 42. G.F. Swift Chicago cattle dealer; recognized that cattle deteriorated as it went east Because of no refrigeration Wanted to dress it at the Chicago stockyards & ship it east How? A rolling refrigerator Developed a cooling system & a fleet of refrigerated cars This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 43. G.F. Swift...Cont’d. Created refrigerated warehouses Wagons distributed meat to local butchers Facilities processed what was left from butchering Dealt other grocery commodities Used vertical integration like Andrew Carnegie This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 44. Mass-Marketing The refrigerated cars worked but the public wasn’t convinced Mass-marketing was needed to change their minds—this was the birth of modern advertising Brand names & billboards were born in the late 19 th century This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 45. Mass-Marketing...Cont’d. By 1900 companies spent $90 million/year for space in newspapers & magazines Adverts urged readers to bathe with Pears’ soap, eat Uneeda biscuits, sew on a Singer machine, snap pictures w/a Kodak camera This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 46. Women to Work During the Industrial Revolution immigrants made up a large # of the urban workforce This was the same during the Gilded Age Women began working in urban jobs during this period as well Over 4 million women worked for wages in 1900 This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 47. Women to Work...Cont’d. Wives were not supposed to work outside the home (especially in middle-class or wealthy families) Older women working outside the home signaled problems (widowed, divorced, etc) Women’s work fell into 3 categories: -1. Maids/domestic servants -2. Teaching, nursing, sales, office work -3. Industry (garment trades/textile mills) This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 48. The Common Worker During the Gilded Age Excess, greed, and classism benefited the wealthy like Morgan, Rockefeller, and Carnegie How did the Gilded Age effect the everyday worker? What did they want? An egalitarian society in which every citizen might hope to become economically independent This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 49. The Knights of Labor This desire led to the formation of the Noble and Holy Order of the Knights of Labor Founded in 1869 as a secret society of garment workers in Philadelphia Spread to other cities by 1878 like the Masons of IOOF This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 50. The Knights of Labor...Cont’d. Their big idea: establish factories and shops owned/run by the employees Public “education” was their main outcome KOL, like trade unions, were favorite causes of radical political parties Communism & Anarchism This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 51. Haymarket Square Riot Anarchy —a stateless/anti-government society Chicago anarchists held public meetings like the fateful meeting in Haymarket Square Large #’s of anarchists/trade unionists, mostly German immigrants, met at Haymarket Square Police moved in to break up the rally... This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 52. Haymarket Square Riot...Cont’d. Someone threw a bomb into the crowd of police, killing and wounded several A small group of anarchists were tried, found guilty, and executed Anti-Union hysteria broke out after Haymarket Square Broke strikes through force, compiled blacklists, & outlawed union activity This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 54. The Homestead Strike Homestead, Penn. Was the site of one of Carnegie’s steel mills Carnegie had always said that workers had the right to organize and it’s wrong to bring in strikebreakers He also believed in making money and believed skilled workers could be replaced by advanced machinery This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 55. The Homestead Strike...Cont’d. Mill was fortified w/tall wooden fence topped w/barbed wire to keep strikebreakers out 2 barges w/armed guards headed up the river toward Homestead to take control of the steelworks Strikers fought back and the Pennsylvania milita was called in Union leaders were arrested on charges of riot, murder, & treason This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 56. The Pullman Strike Pullman, Illinois was a model factory town built by George Pullman, inventor of the sleeping car Panic of 1893 (economic recession) motivated Pullman to cut wages for his workers but not rent A worker’s committee issued a complaint Pullman responded: it’s not my responsibility He then fired the committee This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 57. The Pullman Strike...Cont’d. Pullman workers refused to operate, repair, or maintain the cars RR companies were losing money and attached US Mail cars to every train hauling Pullman cars When strikers stopped the trains the companies appealed to the government This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 58. The Pullman Strike...Cont’d. The federal government said the mail could not be obstructed The leaders of the strike were charged and sentenced w/prison terms The strike fell apart from no leadership It also indicated the ideology of government: The federal government will side w/big business This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com
- 59. The Wizard of Oz as Populism Crazy Theory, Half Truth, or Right On?
- 60. What was Populism? Populism —political ideology supporting the rights and power of the people in their struggle against the elite (worker against tycoon) Populists were largely Midwestern agriculturalists who sided with the Democratic party One major element of the Populist movement was their desire to use silver to equalize the nation’s currency Republicans wanted to keep the gold standard (which we have today)
- 61. What was Populism…Cont’d. The depression of the 1890s reeked havoc on American workers Farm prices bottomed out Union militancy rose among the urban working class Americans wanted a change That change was found in the 1896 election between Republican candidate William McKinley and Populist-Democrat William Jennings Bryan “ The Cross of Gold” L. Frank Baum (author of The Wonderful Wizard of Oz ) was a Populist who supported Bryan
- 62. Populism and Oz: the Symbolism Although some debate exists on the accuracy of the Populism/Oz comparison, the symbolism is certainly evident: Every major character and location can be traced to an element of the Populist movement
- 63. Populism and Oz: the Symbolism…Cont’d. The word “Oz” is the abbreviation of ounce—as in ounce (oz) of gold (the Republican position) Dorothy —represents “everyman” (symbolic of the commoner) Innocent Ability to recognize Oz for its tricks Midwestern (home of Populism)
- 64. Populism and Oz: the Symbolism…Cont’d. Munchkins —represent the “little man” Common laborers Controlled by the Wicked Witch of the EAST (we’ll get to that shortly) “ The Lollipop Guild” Guilds were an early form of unionism
- 65. Populism and Oz: the Symbolism…Cont’d. Scarecrow -the farmer, naïve to the tricks of the world Muted and dumb by the Wicked Witch of the EAST One of the wisest of the traveling companions along the Yellow Brick Road
- 66. Populism and Oz: the Symbolism…Cont’d. Tin Man -the dehumanized industrial worker Becomes mechanical (like industry) Loses his skilled trade Unable to love (his work?) Needs constant oil Needs Standard Oil
- 67. Populism and Oz: the Symbolism…Cont’d. Cowardly Lion -represents William Jennings Bryan Had a “loud roar” Had a good platform Unable to back it up though Parades as a humble king figure
- 68. Populism and Oz: the Symbolism…Cont’d. Wicked Witch of the West —western industrial influence The loss of the common farmer in the west Adoption of industry/urbanization Destroyed by water=pure nature Removal of machinery
- 69. Populism and Oz: the Symbolism…Cont’d. Wicked Witch of the East —represents eastern industrialization Birth of the problem for Populists Killed/destroyed by the innocent farmer’s daughter’s house from the Midwest
- 70. Populism and Oz: the Symbolism…Cont’d. Yellow Brick Road -the gold standard A road paved with gold goes nowhere The Republican platform with their reliance on the gold standard keeps the status quo in Oz
- 71. Populism and Oz: the Symbolism…Cont’d. The Silver Slippers —silver standard (bimetallism) MGM made the slippers red to showcase Technicolor In the original book, published in 1900, the slippers were made of silver
- 72. Populism and Oz: the Symbolism…Cont’d. Winged Monkeys —used in cartoons of the time to ridicule politicians May have represented police/private detective agencies/strike-breakers Wizard of Oz —the president McKinley was often called a wizard of politics















![The Indian Wars...Cont’d. Sioux Chief Red Cloud said in 1870: “ The white children have surrounded me and left me nothing but an island…When we first had all this land we were strong; now we are all melting like snow on a hillside, while you [white Americans] are grown like spring grass.” By the 1870s most Americans agreed Indians should be moved off the plains or concentrated somewhere This Presentation is Available Online at: www.livingamericanhistory.blogspot.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/westwardexpansion-090226121751-phpapp02/85/Westward-Expansion-The-Gilded-Age-16-320.jpg)