Human health & diseases
- 1. Human Health & Diseases Class XII NCERT/ CBSE Shubhadeep Bhattacharjee
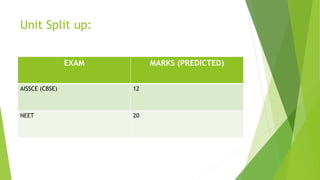
- 2. Unit Split up: EXAM MARKS (PREDICTED) AISSCE (CBSE) 12 NEET 20
- 3. Hitlist: Health & Disease Common diseases in humans Concept of immunity AIDS Cancer Drugs & alcohol
- 4. HEALTH: Physical, mental and social wellbeing DISEASE: Any functional or physical change from the normal state that causes discomfort , or disability, or impairs the health of an organism is called a disease. DISEASES CAUSE DETEREORATION IN HEALTH STATE?????
- 6. INFECTIOUS DISEASE NON-INFECTIOUS DISEASE CONGENITAL DISEASE • Common Cold • Scurvy • Arthritis • Cardio Vascular Diseases • Rickets • Pneumonia • Sickle Cell Anemia • Haemophilia • COVID-19 • Diabetes
- 7. INFECTIOUS DISEASES: PATHOGENS: Micro organisms that can cause a disease ( Bacteria, Virus, Protozoans, Helminths, Fungi etc.) PATHOGEN DISEASE Bacteria Pneumonia, Typhoid Virus Influenza, Small pox, Chicken pox Protozoans Malaria, Amoebiasis Helminths Ascariasis, Filariasis Fungi Ringworm, Athlete’s foot
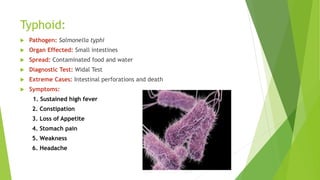
- 8. Typhoid: Pathogen: Salmonella typhi Organ Effected: Small intestines Spread: Contaminated food and water Diagnostic Test: Widal Test Extreme Cases: Intestinal perforations and death Symptoms: 1. Sustained high fever 2. Constipation 3. Loss of Appetite 4. Stomach pain 5. Weakness 6. Headache
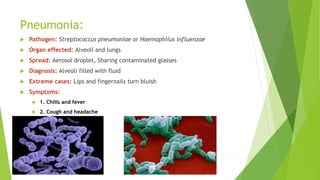
- 9. Pneumonia: Pathogen: Streptococcus pneumoniae or Haemophilus influenzae Organ effected: Alveoli and lungs Spread: Aerosol droplet, Sharing contaminated glasses Diagnosis: Alveoli filled with fluid Extreme cases: Lips and fingernails turn bluish Symptoms: 1. Chills and fever 2. Cough and headache
- 10. Common Cold: Pathogen: Rhinovirus Organ Effected: Nose and upper respiratory tract Spread: Aerosols and contaminated objects Lasts for 3-7 days Symptoms: 1. Hoarseness of throat 2. Nasal congestion and discharge 3. Headache 4. Tiredness
- 11. • Are all micro organisms pathogenic? • Are all pathogens micro organisms?
- 12. Malaria: Pathogen: Plasmodium (P. vivax, P. malaria, P. falciparum) Vector: Female Anopheles mosquito Organ Effected: Liver & RBCs Symptoms: High fever after an incubation period of 14 days Restlessness Loss of appetite Early Symptoms Sleeplessness Muscular pain Headache Late Symptoms Chills
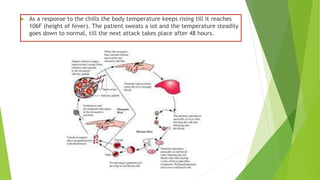
- 13. As a response to the chills the body temperature keeps rising till it reaches 106F (height of fever). The patient sweats a lot and the temperature steadily goes down to normal, till the next attack takes place after 48 hours.
- 14. Plasmodium has two life stages: 1. Asexual Stages: Sporozoites (Human Host) 2. Sexual Stages: Gametocytes (Anopheles Host) • Sporozoites divide asexually to give rise to more sporozoites • Male and female gametocyte fuse together to form sporozoites
- 15. Anti malarial drugs: quinine, chloroquine Killing of mosquitoes by spraying DDT, BHC etc., and use of insect repellents, mosquito nets etc., the disease can be controlled • Sporozoites initially multiply in the liver and then attack the RBCs • Rupture of RBCs releases a toxin called haemozoin, which is responsible for high recurring fever
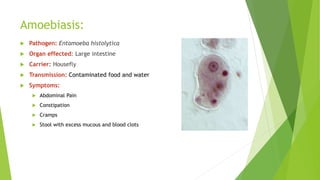
- 16. Amoebiasis: Pathogen: Entamoeba histolytica Organ effected: Large intestine Carrier: Housefly Transmission: Contaminated food and water Symptoms: Abdominal Pain Constipation Cramps Stool with excess mucous and blood clots
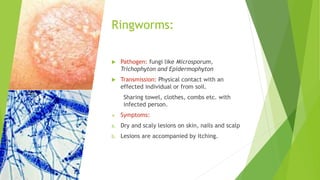
- 17. Ringworms: Pathogen: fungi like Microsporum, Trichophyton and Epidermophyton Transmission: Physical contact with an effected individual or from soil. Sharing towel, clothes, combs etc. with infected person. Symptoms: a. Dry and scaly lesions on skin, nails and scalp b. Lesions are accompanied by itching.
- 18. Ascariasis: Pathogen: intestinal endoparasite of man, Ascaris lumbricoides (Roundworm) Transmission: Contaminated vegetables, fruits and water. Symptoms: a. Abdominal pain b. indigestion c. internal bleeding d. muscular pain e. fever f. anemia g. nausea and headache h. blockage of the intestinal passage.
- 19. Filariasis/ Elephantiasis: Pathogen: Wuchereria bancrofti and Wuchereria malayi (filarial worm) Vector: female Culex mosquito Cause inflammation of the organs in which they live for many years Affect the lymph vessels of the lower limbs. Blocked lymph nodes results in swelling of the legs. External genitalia may also be affected leading to gross deformities.
- 20. Prevention & Control of Infectious Diseases: Maintenance of personal hygiene Maintenance of public hygiene Eradication of vectors and their breeding places Vaccination and immunization programs for diseases like polio, diptheria, tetanus etc. Use of antibiotics and drugs to treat the infected person.
- 21. Quick Revision: Health Disease Types of diseases Pathogens/ vectors/ carriers Bacterial diseases ( Typhoid & Pneumonia) Viral disease ( Common cold) Protozoan disease ( Malaria & Amoebiasis) Fungal Disease ( Ringworm) Helminthic Disease ( Ascariasis & Filariasis) Prevention & control of infectious diseases