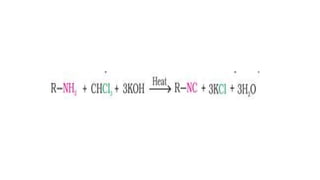Amines class 12 ppt CBSE
- 2. Introduction to amines • Amines constitute an important class of organic compounds derived by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms of ammonia molecule by alkyl/aryl groups. • Amines can be considered as derivatives of ammonia, obtained by replacement of one, two or all the three hydrogen atoms by alkyl and/or aryl groups. For example:
- 3. Structure of amines • Like ammonia, nitrogen atom of amines is trivalent and carries an unshared pair of electrons. Nitrogen orbitals in amines are therefore, sp3 hybridised and the geometry of amines is triagonal pyramidal. • Each of the three sp3 hybridised orbitals of nitrogen overlap with orbitals of hydrogen or carbon depending upon the composition of the amines. • The fourth orbital of nitrogen in all amines contains an unshared pair of electrons. Due to the presence of unshared pair of electrons, the angle C–N–E is the angle less than 109.5.
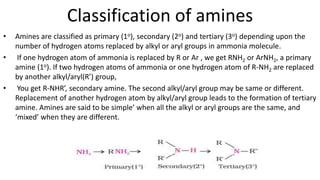
- 4. Classification of amines • Amines are classified as primary (1o), secondary (2o) and tertiary (3o) depending upon the number of hydrogen atoms replaced by alkyl or aryl groups in ammonia molecule. • If one hydrogen atom of ammonia is replaced by R or Ar , we get RNH2 or ArNH2, a primary amine (1o). If two hydrogen atoms of ammonia or one hydrogen atom of R-NH2 are replaced by another alkyl/aryl(R’) group, • You get R-NHR’, secondary amine. The second alkyl/aryl group may be same or different. Replacement of another hydrogen atom by alkyl/aryl group leads to the formation of tertiary amine. Amines are said to be simple’ when all the alkyl or aryl groups are the same, and ‘mixed’ when they are different.
- 5. Nomenclature of amines • In common system, an aliphatic amine is named by prefixing alkyl group to amine, i.e., alkylamine as one word (e.g., methylamine). • In secondary and tertiary amines, when two or more groups are the same, the prefix di or tri is appended before the name of alkyl group. • In IUPAC system, amines are named as alkanamines, derived by replacement of ‘e’ of alkane by the word amine. For example, CH3NH2 is named as methanamine. In case, more than one amino group is present at different positions in the parent chain, their positions are are specified by giving numbers to the carbon atoms bearing –NH2 groups and suitable prefix such as di, tri, etc. is attached to the amine. The letter ‘e’ of the suffix of the hydrocarbon part is retained. • For example, H2N–CH2–CH2–NH2 is named as ethane-1, 2-diamine. • In arylamines, –NH2 group is directly attached to the benzene ring. C6H5NH2 is the simplest example of arylamine. In common system, it is known as aniline. It is also an accepted IUPAC name. • While naming arylamines according to IUPAC system, suffix ‘e’ of arene is replaced by ‘amine’. Thus in IUPAC system, C6H5–NH2 is named as benzenamine.
- 7. Physical properties • Amines are moderately polar substances; they have boiling points that are higher than those of alkanes but generally lower than alcohols of comparable molecular weight. Molecules of primary and secondary amines can form strong hydrogen bonds to each other and to water. • Molecules of tertiary amines can not form hydrogen bonds to each other, but they can form hydrogen bonds to molecules of water or other hydroxylic solvents. • As a result, tertiary amines generally boil at lower temperatures than primary and secondary amines of comparable molecular weight. Therefore, the order of boiling points of isomeric amines is as follows. primary > secondary > tertiary.
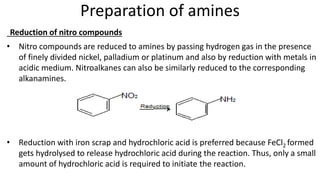
- 8. Preparation of amines Reduction of nitro compounds • Nitro compounds are reduced to amines by passing hydrogen gas in the presence of finely divided nickel, palladium or platinum and also by reduction with metals in acidic medium. Nitroalkanes can also be similarly reduced to the corresponding alkanamines. • Reduction with iron scrap and hydrochloric acid is preferred because FeCl2 formed gets hydrolysed to release hydrochloric acid during the reaction. Thus, only a small amount of hydrochloric acid is required to initiate the reaction.
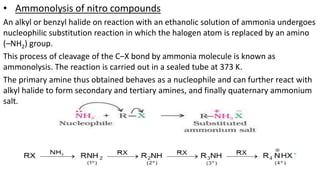
- 9. • Ammonolysis of nitro compounds An alkyl or benzyl halide on reaction with an ethanolic solution of ammonia undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction in which the halogen atom is replaced by an amino (–NH2) group. This process of cleavage of the C–X bond by ammonia molecule is known as ammonolysis. The reaction is carried out in a sealed tube at 373 K. The primary amine thus obtained behaves as a nucleophile and can further react with alkyl halide to form secondary and tertiary amines, and finally quaternary ammonium salt.
- 10. • Ammonolysis has the disadvantage of yielding a mixture of primary, secondary and tertiary amines and also a quaternary ammonium salt. However, primary amine is obtained as a major product by taking large excess of ammonia. • The order of reactivity of halides with amines is RI > RBr >RCl Reduction of nitriles • Nitriles on reduction with lithium aluminium hydride (LiAlH4) or catalytic hydrogenation produce primary amines. This reaction is used for ascent of amine series, i.e., for preparation of amines containing one carbon atom more than the starting amine.
- 11. Reduction of amides • The amides on reduction with lithium aluminium hydride yield amines. Gabriel phthalimide synthesis • Gabriel synthesis is used for the preparation of primary amines. Phthalimide on treatment with ethanolic potassium hydroxide forms potassium salt of phthalimide which on heating with alkyl halide followed by alkaline hydrolysis produces the corresponding primary amine. • Aromatic primary amines cannot be prepared by this method because aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution with the anion formed by phthalimide.
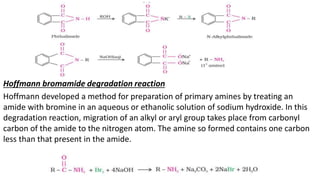
- 12. Hoffmann bromamide degradation reaction Hoffmann developed a method for preparation of primary amines by treating an amide with bromine in an aqueous or ethanolic solution of sodium hydroxide. In this degradation reaction, migration of an alkyl or aryl group takes place from carbonyl carbon of the amide to the nitrogen atom. The amine so formed contains one carbon less than that present in the amide.
- 13. Chemical properties of amines • Difference in electronegativity between nitrogen and hydrogen atoms and the presence of unshared pair of electrons over the nitrogen atom makes amines reactive. • The number of hydrogen atoms attached to nitrogen atom also decides the course of reaction of amines; that is why primary secondary and tertiary amines and differ in many reactions. • Moreover, amines behave as nucleophiles due to the presence of unshared electron pair.
- 14. • Basic character of amines:- Amines, being basic in nature, react with acids to form salts. also aniline + HCl gives anilinium chloride • Amine salts on treatment with a base like NaOH, regenerate the parent amine. • Amine salts are soluble in water but insoluble in organic solvents like ether. This reaction is the basis for the separation of amines from the non basic organic compounds insoluble in water. • The reaction of amines with mineral acids to form ammonium salts shows that these are basic in nature. Amines have an unshared pair of electrons on nitrogen atom due to which they behave as Lewis base. Basic character of amines can be better understood in terms of their Kb and pKb values . • Larger the value of Kb or smaller the value of pKb, stronger is the base. • Aliphatic amines are stronger bases than ammonia due to +I effect of alkyl groups leading to high electron density on the nitrogen atom. • On the other hand, aromatic amines are weaker bases than ammonia due to the electron withdrawing nature of the aryl group. • You may find some discrepancies while trying to interpret the Kb values of amines on the basis of +I or –I effect of the substituents present in amines. Besides inductive effect, there are other effects like solvation effect, steric hinderance, etc., which affect the basic strength of amines
- 16. Structure-basicity relationship of amines • Due to the electron releasing nature of alkyl group, it (R) pushes electrons towards nitrogen and thus makes the unshared electron pair more available for sharing with the proton of the acid. • Moreover, the substituted ammonium ion formed from the amine gets stabilised due to dispersal of the positive charge by the +I effect of the alkyl group. Hence, alkylamines are stronger bases than ammonia. Thus, the basic nature of aliphatic amines should increase with increase in the number of alkyl groups. • This trend is followed in the gaseous phase. The order of basicity of amines in the gaseous phase follows the expected order: tertiary amine > secondary amine > primary amine > NH3. • In the aqueous phase, the substituted ammonium cations get stabilised not only by electron releasing effect of the alkyl group (+I) but also by solvation with water molecules. The greater the size of the ion, lesser will be the solvation and the less stabilised is the ion. The order of stability of ions are as follows:
- 17. • The order of stability of ions are as follows • Decreasing order of extent of H-bonding in water and order of stability of ions by solvation. • Greater is the stability of the substituted ammonium cation, stronger should be the corresponding amine as a base. Thus, the order of basicity of aliphatic amines should be: primary > secondary > tertiary, which is opposite to the inductive effect based order. Secondly, when the alkyl group is small, like –CH3 group, there is no steric hindrance to H-bonding. In case the alkyl group is bigger than CH3 group, there will be steric hinderance to H-bonding. • Therefore, the change of nature of the alkyl group, e.g., from –CH3 to –C2H5 results in change of the order of basic strength. Thus, there is a subtle interplay of the inductive effect, solvation effect and steric hinderance of the alkyl group which decides the basic strength of alkyl amines in the aqueous state. The order of basic strength in case of methyl substituted amines and ethyl substituted amines in aqueous solution is as follows: (C2H5)2NH > (C2H5)3N > C2H5NH2 > NH3 (CH3)2NH > CH3NH2 > (CH3)3N > NH3
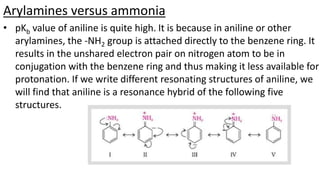
- 18. Arylamines versus ammonia • pKb value of aniline is quite high. It is because in aniline or other arylamines, the -NH2 group is attached directly to the benzene ring. It results in the unshared electron pair on nitrogen atom to be in conjugation with the benzene ring and thus making it less available for protonation. If we write different resonating structures of aniline, we will find that aniline is a resonance hybrid of the following five structures.
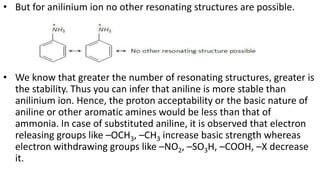
- 19. • But for anilinium ion no other resonating structures are possible. • We know that greater the number of resonating structures, greater is the stability. Thus you can infer that aniline is more stable than anilinium ion. Hence, the proton acceptability or the basic nature of aniline or other aromatic amines would be less than that of ammonia. In case of substituted aniline, it is observed that electron releasing groups like –OCH3, –CH3 increase basic strength whereas electron withdrawing groups like –NO2, –SO3H, –COOH, –X decrease it.
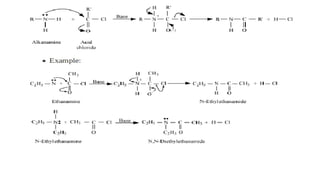
- 20. • Acylation Aliphatic and aromatic primary and secondary amines react with acid chlorides, anhydrides and esters by nucleophilic substitution reaction. This reaction is known as acylation. You can consider this reaction as the replacement of hydrogen atom of –NH2 or >N–H group by the acyl group. The products obtained by acylation reaction are known as amides. The reaction is carried out in the presence of a base stronger than the amine, like pyridine, which removes HCl so formed and shifts the equilibrium to the right hand side.
- 22. • Amines also react with benzoyl chloride (C6H5COCl). This reaction is known as benzoylation. • CH3NH2 + C6H5COCl __>CH3NHCOC6H5 + HCl methanamine + benzoyl chloride __> N − Methylbenzamide • Amines on reaction with carboxylic acids form salts with amines at room temperature. Carbylamine reaction:- Aliphatic and aromatic primary amines on heating with chloroform and ethanolic potassium hydroxide form isocyanides or carbylamines which are foul smelling substances. Secondary and tertiary amines do not show this reaction. This reaction is known as carbylamine reaction or isocyanide test and is used as a test for primary amines.
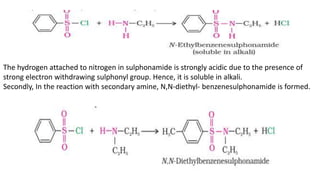
- 24. Reaction with nitrous acid Three classes of amines react differently with nitrous acid which is prepared in situ from a mineral acid and sodium nitrite. (a) Primary aliphatic amines react with nitrous acid to form aliphatic diazonium salts which being unstable, liberate nitrogen gas quantitatively and alcohols (b) Aromatic amines react with nitrous acid at low temperatures (273-278 K) to form diazonium salts. The complex formed when phenyl reacts with amino group is called benzenediazonium chloride. Reaction with arylsulphonyl chloride • Benzenesulphonyl chloride (C6H5SO2Cl), which is also known as Hinsberg’s reagent, reacts with primary and secondary amines to form sulphonamides. (a) The reaction of benzenesulphonyl chloride with primary amine yields N- ethylbenzenesulphonyl amide.
- 25. The hydrogen attached to nitrogen in sulphonamide is strongly acidic due to the presence of strong electron withdrawing sulphonyl group. Hence, it is soluble in alkali. Secondly, In the reaction with secondary amine, N,N-diethyl- benzenesulphonamide is formed.
- 26. • Since N, N-diethylbenzene sulphonamide does not contain any hydrogen atom attached to nitrogen atom, it is not acidic and hence insoluble in alkali. • (c) Tertiary amines do not react with benzenesulphonyl chloride. • This property of amines reacting with benzenesulphonyl chloride in a different manner is used for the distinction of primary, secondary and tertiary amines and also for the separation of a mixture of amines.
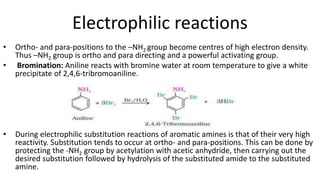
- 27. Electrophilic reactions • Ortho- and para-positions to the –NH2 group become centres of high electron density. Thus –NH2 group is ortho and para directing and a powerful activating group. • Bromination: Aniline reacts with bromine water at room temperature to give a white precipitate of 2,4,6-tribromoaniline. • During electrophilic substitution reactions of aromatic amines is that of their very high reactivity. Substitution tends to occur at ortho- and para-positions. This can be done by protecting the -NH2 group by acetylation with acetic anhydride, then carrying out the desired substitution followed by hydrolysis of the substituted amide to the substituted amine.
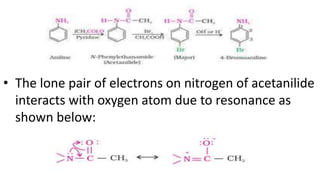
- 28. • The lone pair of electrons on nitrogen of acetanilide interacts with oxygen atom due to resonance as shown below:
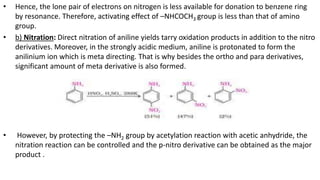
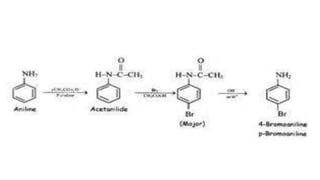
- 29. • Hence, the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen is less available for donation to benzene ring by resonance. Therefore, activating effect of –NHCOCH3 group is less than that of amino group. • b) Nitration: Direct nitration of aniline yields tarry oxidation products in addition to the nitro derivatives. Moreover, in the strongly acidic medium, aniline is protonated to form the anilinium ion which is meta directing. That is why besides the ortho and para derivatives, significant amount of meta derivative is also formed. • However, by protecting the –NH2 group by acetylation reaction with acetic anhydride, the nitration reaction can be controlled and the p-nitro derivative can be obtained as the major product .
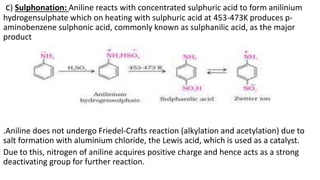
- 31. c) Sulphonation: Aniline reacts with concentrated sulphuric acid to form anilinium hydrogensulphate which on heating with sulphuric acid at 453-473K produces p- aminobenzene sulphonic acid, commonly known as sulphanilic acid, as the major product .Aniline does not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction (alkylation and acetylation) due to salt formation with aluminium chloride, the Lewis acid, which is used as a catalyst. Due to this, nitrogen of aniline acquires positive charge and hence acts as a strong deactivating group for further reaction.
- 32. Diazonium salts The diazonium salts have the general formula R N2 X where R stands for an aryl group and X ion may be Cl Br, HSO4, BF4 , etc. They are named by suffixing diazonium to the name of the parent hydrocarbon from which they are formed, followed by the name of anion such as chloride, hydrogensulphate, etc. The + group is called diazonium N2 group. For example, C6H5 N2 Cl is named as benzenediazonium chloride and C6H5N2+HSO4 is known as benzenediazonium hydrogensulphate .
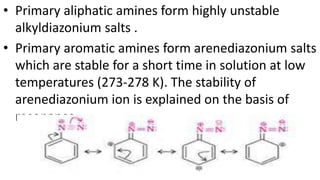
- 33. • Primary aliphatic amines form highly unstable alkyldiazonium salts . • Primary aromatic amines form arenediazonium salts which are stable for a short time in solution at low temperatures (273-278 K). The stability of arenediazonium ion is explained on the basis of resonance.
- 34. Methods of preparation of diazonium salts • Benzenediazonium chloride is prepared by the reaction of aniline with nitrous acid at 273-278K. • Nitrous acid is produced in the reaction mixture by the reaction of sodium nitrite with hydrochloric acid. • The conversion of primary aromatic amines into diazonium salts is known as diazotisation. Due to its instability, the diazonium salt is not generally stored and is used immediately after its preparation. • C6H5NH2 + NaNO2 + 2HCl > C6H5N2Cl+ NaCl + 2H2O
- 35. Physical properties • Benzenediazonium chloride is a colourless crystalline solid. It is readily soluble in water and is stable in cold but reacts with water when warmed. It decomposes easily in the dry state. Benzenediazonium fluoroborate is water insoluble and stable at room temperature.
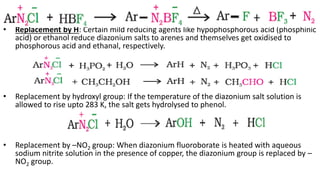
- 36. Chemical properties • The reactions of diazonium salts can be broadly divided into two categories, namely (A) reactions involving displacement of nitrogen and (B) reactions involving retention of diazo group. Reactions involving displacement of nitrogen • Diazonium group being a very good leaving group, is substituted by other groups such as Cl–, Br– I– CN– and OH– which displace , nitrogen from the aromatic ring. The nitrogen formed escapes from the reaction mixture as a gas. 1. Replacement by halide or cyanide ion: The Cl–, Br– and CN– nucleophiles can easily be introduced in the benzene ring in the presence of Cu(I) ion. This reaction is called Sandmeyer reaction.
- 37. • Alternatively, chlorine or bromine can also be introduced in the benzene ring by treating the diazonium salt solution with corresponding halogen acid in the presence of copper powder. This is referred as Gatterman reaction. • The yield in Sandmeyer reaction is found to be better than Gattermann reaction. Replacement by iodide ion: Iodine is not easily introduced into the benzene ring directly, but, when the diazonium salt solution is treated with potassium iodide, iodobenzene is formed. • Replacement by fluoride ion: When arenediazonium chloride is treated with fluoroboric acid, arene diazonium fluoroborate is precipitated which on heating decomposes to yield aryl fluoride.
- 38. • Replacement by H: Certain mild reducing agents like hypophosphorous acid (phosphinic acid) or ethanol reduce diazonium salts to arenes and themselves get oxidised to phosphorous acid and ethanal, respectively. • Replacement by hydroxyl group: If the temperature of the diazonium salt solution is allowed to rise upto 283 K, the salt gets hydrolysed to phenol. • Replacement by –NO2 group: When diazonium fluoroborate is heated with aqueous sodium nitrite solution in the presence of copper, the diazonium group is replaced by – NO2 group.
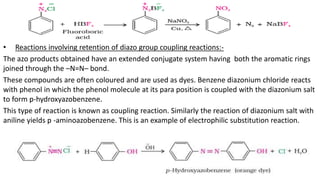
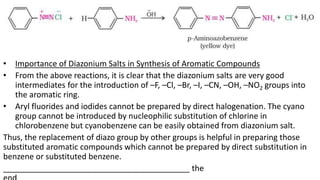
- 39. • Reactions involving retention of diazo group coupling reactions:- The azo products obtained have an extended conjugate system having both the aromatic rings joined through the –N=N– bond. These compounds are often coloured and are used as dyes. Benzene diazonium chloride reacts with phenol in which the phenol molecule at its para position is coupled with the diazonium salt to form p-hydroxyazobenzene. This type of reaction is known as coupling reaction. Similarly the reaction of diazonium salt with aniline yields p -aminoazobenzene. This is an example of electrophilic substitution reaction.
- 40. • Importance of Diazonium Salts in Synthesis of Aromatic Compounds • From the above reactions, it is clear that the diazonium salts are very good intermediates for the introduction of –F, –Cl, –Br, –I, –CN, –OH, –NO2 groups into the aromatic ring. • Aryl fluorides and iodides cannot be prepared by direct halogenation. The cyano group cannot be introduced by nucleophilic substitution of chlorine in chlorobenzene but cyanobenzene can be easily obtained from diazonium salt. Thus, the replacement of diazo group by other groups is helpful in preparing those substituted aromatic compounds which cannot be prepared by direct substitution in benzene or substituted benzene. __________________________________________ the