Negotiable instruments act 1881
- 1. The Negotiable Instruments Act 1881
- 2. Negotiable Instrument • According to Section 13(i) “ a negotiable instrument means a promissory note, bill of exchange or cheque payable either on order or to bearer”. • An instrument may be negotiable either by 1. Statute : Promissory Notes , bills of exchange and cheques are negotiable instruments under Negotiable Instruments Act 1881 . 2. By Usage : Bank Notes , Bank Drafts , scripts, treasury Bills etc
- 3. Transfer by Negotiation • Negotiation is a transfer of an instrument from one person to another in such a manner as to express title & to represent the transferee the holder thereof. • Passing of possession • With intention to pass title • Must be transferred in such a manner that the transferee becomes holder thereof.
- 4. Methods of Negotiation 1. Negotiation by delivery 2. Negotiation by endorsement & delivery 3. Property is transferred to the endorsee 4. Endorsee get right to negotiate the instrument, sue on instrument.
- 5. Characteristics • It is freely transferable • Better title • Right to sue • A negotiable instrument can be transferred any number of times till its maturity • A negotiable instrument is subject to certain presumptions • Presumptions – certain presumptions as to consideration, reasonable time etc., apply to all negotiable instruments.
- 6. Presumptions 1. Consideration : Every negotiable instrument is deemed to have been drawn and accepted , endorsed, negotiated, or transferred for consideration 2. Date : Every negotiable instrument must bear the date on which it is made or drawn 3. Acceptance : Every Bill of exchange was accepted within a reasonable time after the date mentioned therein and before the date of its maturity 4. Transfer : Every transfer should be made before the expiry
- 7. Meaning of Endorsement • When a maker or holder writes the person’s name on the face or back of the instrument & puts his signatures thereto for the purpose of negotiation, it is called ‘endorsement’. • Person who signs – endorser • To whom it is endorsed – endorsee. • A legal term that refers to the signing of a document which allows for the legal transfer of a negotiable from one party to another. • When an employer signs a check, they are endorsing the transfer of money from the business accounts to the account of the employee.
- 8. Essentials of valid endorsement 1. On the back or face of the instrument. 2. Must be made by maker or holder. 3. Must be properly signed by the endorser. 4. It must be for the entire negotiation instrument. 5. No specific form of words are necessary for endorsement.
- 9. Kinds of endorsement 1. Blank or general endorsement – where endorsee simply puts his signature on the back of the instrument without writing name of the person in whose favor the instrument is endorsed. 2. Special or full endorsement – An endorsement with the direction to pay amount mentioned in the instrument to a specified person or his order & the endorser writes his signature under it. 3. Partial endorsement – When an endorser is willing to transfer to an endorsee only a part of the amount of the instrument. Such an endorsement does not operate as a negotiation of the instrument.
- 10. • The instrument is therefore payable to the bearer • Restrictive endorsement – An endorsement is said to be restrictive if it prohibits or restricts the further negotiability of the instrument. The holder of such an instrument can only receive the payment but he cannot negotiate it further. An instrument can be made restrictive only by expressed words. • Conditional endorsement – It limit the liability of the endorser. E.G. – “ Pay A or order on his marrying B”.
- 11. Effects of Endorsement • The property in instrument is transferred from endorser to endorsee. • The endorsee gets right to negotiate the instrument further. • The endorsee get the right to sue in his own name to all other parties.
- 12. Promissory Notes • Section 4 defines it as, “ A promissory note is an instrument in writing containing an unconditional undertaking, signed by the maker, to pay a certain sum of money only to or to the order of a certain person or to the bearer of the instrument”. • The person who makes the promissory note is called the maker. • The person to whom payment is to be made is called the payee. e.g. – • I promise to pay B or order rs. 500 • I promise to pay B Rs.500 on D’ death, provided D leaves me enough to pay that sum
- 13. Essentials of Promissory Note • It must be in writing • It must contain express promise to pay :- ‘I am liable to pay’ • The promise to pay must be unconditional • It must be signed by maker • The maker must be certain- It must describe the name & designation of the maker, sum of money • There are 2 parties involved i.e. maker and the payee • The payee must be certain- It is essential that it must contain a promise to pay some person ascertained by name or designation. • The sum payable must be certain • The payment must be in legal money • A currency note is not a promissory note
- 14. Bill of Exchange • Section 5, is defined as “A bill of exchange is an instrument in writing containing an unconditional order, signed by the maker, directing a certain person to pay a certain sum of money only to or to the order of a certain person or to the bearer of the instrument”. • Parties to bill of exchange : • Drawer – The person who makes/orders to pay bill of exchange. • Drawee – The person who is directed to pay on bill. On acceptance he becomes acceptor. • Payee – The person to whom the payment is to be made. • Drawer & Payee can be the same person. • X sells goods worth Rs. 2000 to Y & allow him 3 months time to pay the price. X then draws a bill on Y “ Three months after date, pay to my order the sum of Rs. 2000 for value received”. X is drawer . Y is Drawee.
- 15. Essential of Bills of Exchange • It must be in writing • It must contain an order to pay and a promise or request • The order must be unconditional • There must be 3 parties i.e. : drawer, drawee, and payee • The parties must be certain • It must be signed by the drawer • Number, date and place are not essential
- 16. Cheques • Section 6, defines it as “ A cheque is a bill of exchange drawn on a specified banker & not expressed to be payable otherwise than on demand”. • It is always drawn on a bank • It is payable to bearer on demand • Parties To Cheque: 1. Drawer – who makes the cheque 2. Payee – to whom payment is to be made 3. Drawee – Bank .
- 17. Meaning of Crossing of Cheque • Crossing of a cheque is a unique feature associated with a cheque affecting to a certain level the responsibility of the paying Banker and also its negotiable Character. • Crossing of a Cheque is a direction to a particular Banker by the Drawer that Payment should not be made across the Counter. The payment on the crossed Cheque can be collected only through a Banker. • Crossing of the Cheque is affected by drawing two parallel Transverse lines . • The Cheque that is not crossed is an open Cheque.
- 18. Types of cheque • There are two types of cheque: 1. Open cheque – those which can be en cashed across the counter of the bank. Liable to great risk if stolen or lost. Finder can get payment from bank. 2. Crossed cheque – which bears two transverse lines with or without the words “ & co.”
- 19. Various kinds of Crossing 1. General Crossing:- which bears across its face the words “ & co.” or the words “not negotiable”. For general crossing two transverse lines on the face of cheque are essential. The paying banker shall pay only to a banker. There are two sloping parallel lines, marked across its face • The cheque bears an short form "& Co. "between the two parallel lines • The cheque bears the words "A/c. Payee" between the two parallel lines. • The cheque bears the words "Not Negotiable" between the two parallel lines.
- 20. Specimen of General Crossing
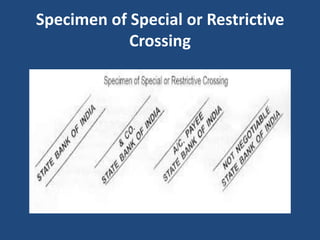
- 21. 2. Special or Restrictive Crossing :- When a particular bank's name is written in between the two parallel lines the cheque is said to be specially crossed. Where a cheque bears across its face an addition the name of banker either with or without the words “ not negotiable”. It contains: • The name of the banker across the face of cheque. • With the words “ not negotiable” • In addition to the word bank, the words "A/c. Payee Only", "Not Negotiable" may also be written. The payment of such cheque is not made unless the bank named in crossing is presenting the cheque. The effect of special crossing is that the bank makes payment only to the banker whose name is written in the crossing. Specially crossed cheques are more safe than a generally crossed cheques.
- 22. Specimen of Special or Restrictive Crossing
- 23. Why Crossing of Cheque is being used • The important usefulness of a crossing cheque is that it cannot be covered at the counter but can be collected only by a bank from the drawee bank. • Crossing provides a protection and safeguard to the owner of the cheque as by securing payment through a banker it can be easily detected to whose use the money is received. Where the cheque is crossed the paying banker shall not pay it except to a banker. • In case of not negotiable crossing the person holding such a cheque gets no better title than that of his transfer and cannot suggest a better title to his own transferee. In case of 'account payee' only crossing, a direction is given to the collecting banker to collect cheque and to place the amount to the credit of the payee only. • A special crossing makes the cheque more safe than a general crossing because the payee or holder cannot receive payment except through the banker named on the cheque.
- 24. Who can cross a Cheque 1. The drawer of a Cheque 2. Holder of the Cheque 3. The Banker in whose favor the cheque has been crossed specially
- 25. Promissory Note Bill of Exchange 1. It contains a promise to pay. 1. It contains an order to pay. 2. It is presented for payment 2. It is required to be accepted either without any previous by the drawee or by some one else acceptance by the maker. on his behalf, before it can be presented for payment. 3. It cannot be made payable to the maker himself. The maker 3. The drawer and payee or the and the payee cannot be the drawee and the payee may be the same person. same person. 4. There are three parties, drawer, 4. In the case of a promissory drawee and payee. note there are only two parties, the maker and the 5. A bill of exchange cannot be payee. drawn conditionally, but it can be accepted conditionally with the 5. A promissory note can never consent of the holder. be conditional. 6. A notice of dishonour must be 6. In case of dishonour no notice given in case of dishonour of a Bills of dishonour is required to be of Exchange. given by the Holder
- 26. Cheque Bill of exchange 1. Drawee: Cheque can be drawn 1. The drawee may be any person. only on a banker. 2. A bill may be drawn payable on 2. Time of payment: A cheque is demand or on expiry of certain payable on demand. period after date or sight. 3. Grace period: Cheque is payable 3. While calculating maturity three on demand and no grace period is day’s grace is allowed. allowed. 4. A notice of dishonour is required. 4. Notice of dishonour: Notice of 5. Bills require presentment for dishonour is not necessary. acceptance and it is better to 5. Acceptance: A cheque is not present them for acceptance even required to be presented for when it is not essential to do so. acceptance. It needs to be 6. A bill of exchange cannot be presented only for payment. crossed. 6. Crossing: A cheque may be 7. A bill may be drawn for any period. crossed. 7. Validity period: A cheque is usually valid for a period of six months.