Working of digital camera
- 1. Working of Digital CameraWorking of Digital Camera 1
- 2. Brief History In 4th century BC mozi invented camera of Obscura. 2 Figure: 1 Camera of Obscura
- 3. 1490, Leonardo da Vinci 1724, Heinrich Schulze and 1822, Nicephore invented Heliography. 1833, Louis Daguerre invented Daguerreotype. 1839, Robert Cornelius took first selfie. 1840, Henry Fox Talbot invented Calotype. 1841, Sir John Hershal gives term photography. 1957, Russel Kirsch generated first digital image. 3 Figure: 2 Selfie of Robert Cornelius using Daguerreotype Contd.
- 4. 1975, Steve Sasson invented first digital camera. 4 Figure: 3 Steven Sasson with first digital camera(left) and first digital image taken by a digital camera(right) Source: www.Wikipedia.com Contd.
- 5. Digital camera • Digital camera is nothing but a box with a hole, you may find some other parts which helps in better functioning of camera but even today all the cameras are based on the basic principle of camera of obscura. • Digital camera sample light from our world, or outer space, spatially, tonally and by time. • Digital camera stores image as array of numbers which can only be read using computer. • Digital camera work in three phases: (i) Focus light on sensor in adequate amount. (ii) Store electrical signal generated by sensor on any storing unit. (iii) Show the image on digital screen using computer. 5
- 6. External parts of digital camera 6 Figure: 4 External parts of digital camera
- 7. Types of Digital Camera Compact SLR Mirrorless interchangeable-lens cameras Digital single-lens reflex camera (DSLR) Digital Single Lens Translucent (DSLT) cameras Line-scan camera Infrared camera 7 Figure: 5 Compact camera(above) and DSLR(below) Source: www.Wikipedia.com
- 8. Working of digital camera • A digital camera takes light and focuses it via the lens onto a sensor made out of silicon. It is made up of a grid of tiny photosites that are sensitive to light. Each photosite is usually called a pixel, a contraction of "picture element".. • Each photosite on a CCD or CMOS absorbs photons and releases electrons through the photoelectric effect. The electrons are stored in a well as an electrical charge that is accumulated over the length of the exposure. • The charge that is generated is proportional to the number of photons that hit the sensor. • This charge is then amplified and sent to A-to-D converter, which gives DN to voltage on basis of gain factor, this is called stepping. 8
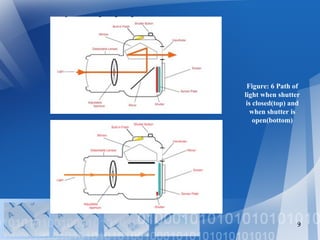
- 9. 9 Figure: 6 Path of light when shutter is closed(top) and when shutter is open(bottom)
- 10. Digital image Spatial sampling: A digitized image is made up of a grid of pixels which are represented by numbers. The numbers specify the pixel's location in the grid, and the brightness of the red, green and blue colour channels. Tonal sampling: Digital camera measure light and break its continuously varying tones into discrete steps. 10 Figure: 7 Spatial sampling(top) and tonal sampling(bottom)
- 11. Numbers: Digital image is saved in numbers which makes working easier. Linear vs Non linear : Images are stored after non-linear stretching. 11 Saving image Figure: 8 Difference between linear and non-linear stretch.
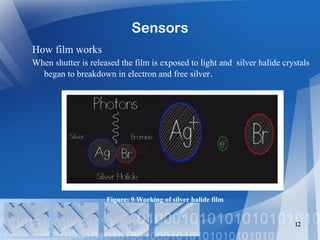
- 12. Sensors How film works When shutter is released the film is exposed to light and silver halide crystals began to breakdown in electron and free silver. 12 Figure: 9 Working of silver halide film
- 13. Digital Sensor •A digital sensor is based on photodiode which converts light energy to electrical energy, a photodiode is a doped semi-conductor mostly silicon •The P-type and N-type semi-conductor can be combined to make a PN- junction 13 Figure: 10 PN-junction
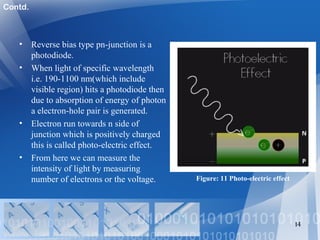
- 14. • Reverse bias type pn-junction is a photodiode. • When light of specific wavelength i.e. 190-1100 nm(which include visible region) hits a photodiode then due to absorption of energy of photon a electron-hole pair is generated. • Electron run towards n side of junction which is positively charged this is called photo-electric effect. • From here we can measure the intensity of light by measuring number of electrons or the voltage. 14 Figure: 11 Photo-electric effect Contd.
- 15. CCD & CMOS • CCD(Charged Coupled Device) CCD uses no wire instead it uses a single silicon slab divided with insulating channels, the slab is then coated with thin layer of silicon oxide and tiny strips of aluminium is laid perpendicular to the channel. 15 Figure: 12 Working of CCD
- 16. • CMOS(Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) Like CCD, a CMOS sensor is made out of single piece of silicon. But instead of shuttling electron row by row, each pixel has a small capacitor and signal amplifier. This amplified voltage is sent down through tiny wires into a bus and processed in parallel. 16 Figure: 13 Working of CMOS Contd.
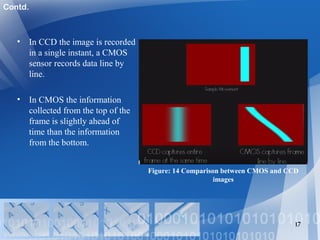
- 17. • In CCD the image is recorded in a single instant, a CMOS sensor records data line by line. • In CMOS the information collected from the top of the frame is slightly ahead of time than the information from the bottom. 17 Figure: 14 Comparison between CMOS and CCD images Contd.
- 18. Colour Image • In 1861, Maxwell used RGB i.e. red, green and blue filters separetely to capture image of a ribbon, on combining these images what he gets was the first ever color image. 18 Figure: 15 Maxwell setup to generate colour image(left) and world’s first ever colour image(right)
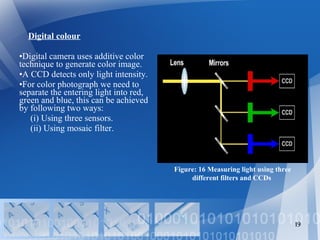
- 19. Digital colour •Digital camera uses additive color technique to generate color image. •A CCD detects only light intensity. •For color photograph we need to separate the entering light into red, green and blue, this can be achieved by following two ways: (i) Using three sensors. (ii) Using mosaic filter. 19 Figure: 16 Measuring light using three different filters and CCDs
- 20. • In consumer cameras the single CCD is covered with a filter with red, green and blue pixel sized section. • This creates an as a mosaic of these three colors. • The camera applies an algorithm to estimate correct color for each pixel. 20 Figure: 17 Mosaic filter to take colour photo using single CCD Contd.
- 21. 21
- 22. Reference Internet Document 1. How Digital Cameras Work (2015). Available online at http://www.astropix.com/HTML/I_ASTROP/HOW.HTM, updated on 2/2/2015, checked on 10/22/2016. Abstract: How Digital Cameras Work Keywords: How Digital Cameras Work Internet Document Wikipedia (Ed.) (2016): 2. Calotype - Wikipedia. Available online at https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?oldid=741202483, updated on 10/18/2016, checked on 10/22/2016. Internet Document Wikipedia (Ed.) (2016): 3. Digital camera - Wikipedia. Available online at https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?oldid=745146118, updated on 10/19/2016, checked on 10/22/2016. Internet Document Wikipedia (Ed.) (2016): 4. Daguerreotype - Wikipedia. Available online at https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?oldid=745632006, updated on 10/22/2016, checked on 10/22/2016. Internet Document Wikipedia (Ed.) (2016): 5. Heliography - Wikipedia. Available online at https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?oldid=745617005, updated on 10/22/2016, checked on 10/22/2016. 22
- 23. Thank You 23