Unit 2
- 1. Unit-2
- 2. Assessment of Term loan & working capital limits
- 3. Term loan Provided for medium & long term ( 3 to 15 years) periods for new / existing projects for expansion / diversification Repayment is for specific period with initial holiday period Secured by fixed assets such as land/ building/ plant / machinery/ other fixed assets Basic aspect in T L is that the borrower should repay the amount with interest from the anticipated income earned from the assets acquired. Technical & economic viability of the project is a must for considering the term loan. In India, the commercial banks extend term loan along with other banks & F I’s in the Consortium / multiple banking modes.
- 4. Term loan appraisal No item to be ignored in project financing Costs shown should be true & not overstated. Three sets of quotation from various suppliers to be obtained Suppliers details and credibility need to be verified Building construction estimates to be properly vetted Funds to be released based on progress of the work. Security coverage is to be assessed.
- 5. Term loan appraisal Technical feasibility Commercial viability Managerial competence Financial viability Technology / process Indian/ foreign/ Collaboration back up arrangement Infrastructure Availability of land / R M / transport/ power / water Pollution/ Project implementation E I C analysis Demand/ supply of the product Competition/ market Marketing abilities Product / service differentiation Organization set up CCC of the borrower finance, management Operations H R Qualified technical persons Cost of the project & means of finance Production/ profitability Cash flow/ funds flow Projected balance sheet profitability statements B E P / CMA
- 6. Cost of project Land (inc dev charges) Building / Machinery (inc fright / transp. erection charges) Other fixed assets Technical Know- how Consultancy charges Preliminary expenses Contingent expenses Working capital margin Total Means of Finance Capital (equity) USL from others Term loan from bank/s Term loan from F I’s Subsidy from Government (if any) Total
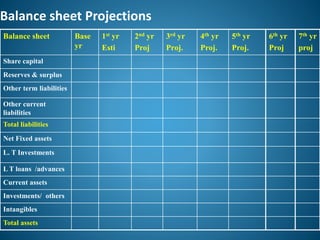
- 7. Balance sheet Projections Balance sheet Base yr 1st yr Esti 2nd yr Proj 3rd yr Proj. 4th yr Proj. 5th yr Proj. 6th yr Proj 7th yr proj Share capital Reserves & surplus Other term liabilities Other current liabilities Total liabilities Net Fixed assets L. T Investments L T loans /advances Current assets Investments/ others Intangibles Total assets
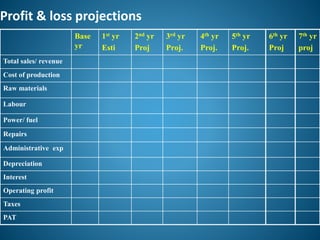
- 8. Profit & loss projections Base yr 1st yr Esti 2nd yr Proj 3rd yr Proj. 4th yr Proj. 5th yr Proj. 6th yr Proj 7th yr proj Total sales/ revenue Cost of production Raw materials Labour Power/ fuel Repairs Administrative exp Depreciation Interest Operating profit Taxes PAT
- 9. Specific Ratios for term loan Debt-equity= long term liabilities / Net worth ( 2 to 3 ) Debt to total funds ratio= L T Debts / share holders funds + Long term debts Debt to total asset ratio= Total debt/ total assets Interest coverage ratio= EBIT/ fixed interest charges. ( 1.5 to 2 ) DSCR= PAT + Depreciation + Interest on Term Loans ( 1.5 to 2 ) Interest on term Loan + Term Loan installments B E P= Fixed costs / Contribution (Sales – Variable Costs ) For long term projects - IRR, PBP & N P V is also calculated
- 10. Case studies
- 11. Working capital Types of working capital provided by Indian Banks are cash credit (Open/ Key) / overdraft / Bills discounting or purchase , STL Cash credit / bills limits are assessed based on the production/ sales/inventory/ past credit limits. Customer allowed to draw the amount from the cash credit account as per his requirement & also deposit the amount based on the surplus funds available. Cash credit / overdrafts are running accounts & the credits in the account should reflect the sales of the company. The drawals permitted to the extent of the drawing power D P is calculated based on the stock statement submitted on monthly and suitable margins are maintained for RM/ SFG/ FG/ B D
- 12. Working capital (cont’d) Interest is charged on the actual usage of the limit. There are three methods of working capital assessment. The turn over method (Nayak committee) , the inventory method & II method of lending (Chore committee) The turn over method / inventory method is normally used for working capital limits up to Rs 5 crs & second method thereafter. If the operating cycle is three months & less , the turnover method is followed & inventory method for more than three months . It should be ensured that the projected turn over is following similar trend as per the last three years. Any deviation may need a closer look for further inputs. Operating cycle method is applied
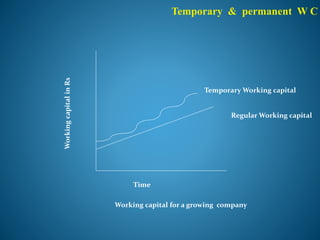
- 13. Temporary & permanent W C WorkingcapitalinRs Time Regular Working capital Temporary Working capital Working capital for a growing company
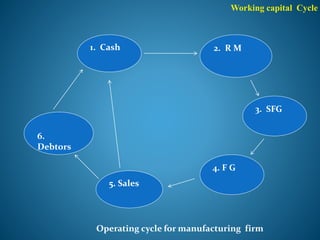
- 14. Working capital Cycle 1. Cash 4. F G 3. SFG 6. Debtors 5. Sales 2. R M Operating cycle for manufacturing firm
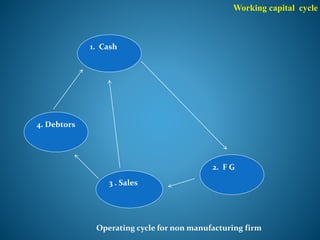
- 15. Working capital cycle 1. Cash 2. F G 4. Debtors 3 . Sales Operating cycle for non manufacturing firm
- 16. Factors influencing Working capital Nature of business Size of the business Production cycle process Production policy Terms of purchase & sales Business cycle ( Up ward/ down ward) Growth & expansion Availability of R M Profit level Operating efficiency Availability of credit
- 17. Working capital (cont’d) Turn over method (Nayak committee ) Operating cycle of three months & less 25% of the projected turn over Minimum working capital margin ( NWC) - 5% of the projected sales Borrower has to bring additional margin if it is less than the prescribed limit Working capital eligibility = (25 % of projected turn over – min NWC or actual NWC ) which ever is less NWC = Current assets - current liability
- 18. Working capital (cont’d) Inventory method (Operating cycle of more than three months ) 1 Build up of current assets 2 Build up of current liabilities (other than Bank borrowings for W C) 3 Working capital gap ( 1-2) 4 Actual NWC 5 Required NWC ( min 15% of current assets ) 6 Maximum permissible bank borrowings ( 3-4 ) or ( 3-5) which ever is less 7 Margin to be brought in ( 5-4) The minimum stipulated margins can vary from banks to banks based on the credit policy guidelines Ex; ( It can be 15% / 20% / 25% )
- 19. Working capital (cont’d) II method of lending (Chore committee ) for credit limits above Rs 5 crs 1 Build up of current assets Amt 2 Build up of current liabilities (other than Bank borrowings for W C) 3 Working capital gap ( 1-2) 4 Actual NWC 5 Required NWC ( min 25% of current assets )(excluding export receivables) 6 Maximum permissible bank borrowings ( 3-4 ) or ( 3-5) which ever is less 7 Margin to be brought in ( 5-4) Borrower provides the required CA , CL for the next year based on the past performance in CMA . The build up has to be in line with past Min 25% of the Current assets has to provided as NWC by the borrower .
- 20. Case studies
- 21. NON Fund based limits- L C Parties to LC 1. Applicant/ Importer 2. Beneficiary/ Exporter 3. Issuing bank / Importers bank 4. Advising bank / Exporters bank
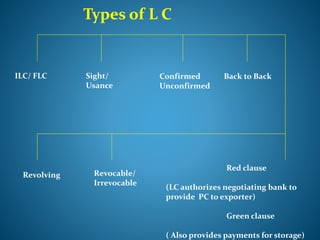
- 22. Types of L C ILC/ FLC Sight/ Usance Revocable/ Irrevocable Confirmed Unconfirmed Back to Back Red clause (LC authorizes negotiating bank to provide PC to exporter) Green clause ( Also provides payments for storage) Revolving
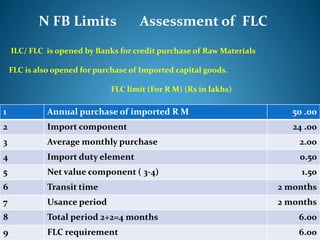
- 23. N FB Limits Assessment of FLC ILC/ FLC is opened by Banks for credit purchase of Raw Materials FLC is also opened for purchase of Imported capital goods. FLC limit (For R M) (Rs in lakhs) 1 Annual purchase of imported R M 50 .00 2 Import component 24 .00 3 Average monthly purchase 2.00 4 Import duty element 0.50 5 Net value component ( 3-4) 1.50 6 Transit time 2 months 7 Usance period 2 months 8 Total period 2+2=4 months 6.00 9 FLC requirement 6.00
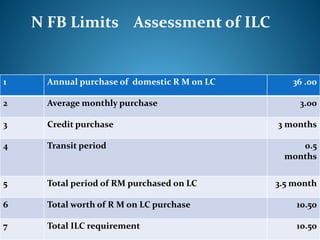
- 24. N FB Limits Assessment of ILC 1 Annual purchase of domestic R M on LC 36 .00 2 Average monthly purchase 3.00 3 Credit purchase 3 months 4 Transit period 0.5 months 5 Total period of RM purchased on LC 3.5 month 6 Total worth of R M on LC purchase 10.50 7 Total ILC requirement 10.50
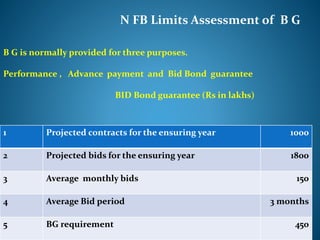
- 25. N FB Limits Assessment of B G B G is normally provided for three purposes. Performance , Advance payment and Bid Bond guarantee BID Bond guarantee (Rs in lakhs) 1 Projected contracts for the ensuring year 1000 2 Projected bids for the ensuring year 1800 3 Average monthly bids 150 4 Average Bid period 3 months 5 BG requirement 450
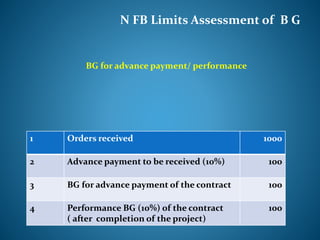
- 26. N FB Limits Assessment of B G 1 Orders received 1000 2 Advance payment to be received (10%) 100 3 BG for advance payment of the contract 100 4 Performance BG (10%) of the contract ( after completion of the project) 100 BG for advance payment/ performance
- 27. Case studies
- 28. N F B Limit- DPG