Fundamentals of photography
- 1. All the photographs featured in this presentation are the property of Zain Abdullah unless otherwise stated - Zain Abdullah l flickr.com/photos/mzabdullah
- 2. What we basically aim for when taking picture is a correctly exposed picture. Good picture = Correctly exposed picture Correctly exposed or optimally exposed picture means white area appears white, black area appears black in the picture Exposure > Basics
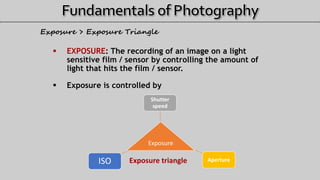
- 3. EXPOSURE: The recording of an image on a light sensitive film / sensor by controlling the amount of light that hits the film / sensor. Exposure is controlled by Exposure > Exposure Triangle Exposure Shutter speed ApertureISO Exposure triangle
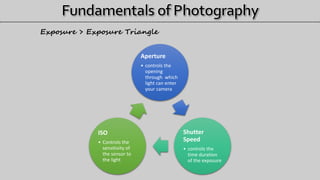
- 4. Aperture • controls the opening through which light can enter your camera Shutter Speed • controls the time duration of the exposure ISO • Controls the sensitivity of the sensor to the light Exposure > Exposure Triangle
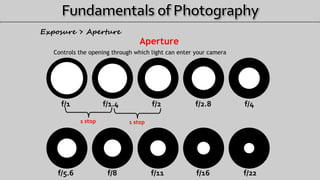
- 5. Aperture Controls the opening through which light can enter your camera f/1 f/1.4 f/2 f/2.8 f/4 f/5.6 f/8 f/11 f/16 f/22 1 stop Exposure > Aperture 1 stop
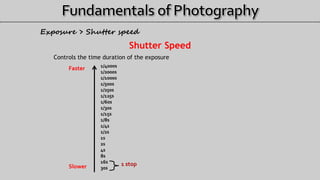
- 6. Shutter Speed Controls the time duration of the exposure 1/4000s 1/2000s 1/1000s 1/500s 1/250s 1/125s 1/60s 1/30s 1/15s 1/8s 1/4s 1/2s 1s 2s 4s 8s 16s 30s Faster Slower 1 stop Exposure > Shutter speed
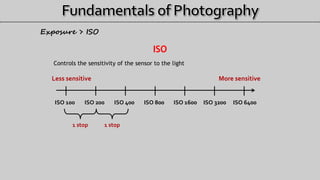
- 7. ISO Controls the sensitivity of the sensor to the light ISO 100 ISO 200 ISO 400 ISO 800 ISO 1600 ISO 3200 ISO 6400 More sensitiveLess sensitive 1 stop Exposure > ISO 1 stop
- 8. • One can therefore use many combinations of the above three settings to achieve the optimal exposure. • ISO 100 | Shutter speed: 1/125s | Aperture: f16 • ISO 800 | Shutter speed: 1/1000s | Aperture: f16 • ISO 100 | Shutter speed: 1/1000s | Aperture: f5.6 • ISO 400 | Shutter speed: 1/2000s| Aperture: f8 • The key, however, is knowing which trade-offs to make, since each setting also influences other image properties. • For example: • aperture affects depth of field • shutter speed affects motion blur • ISO speed affects image noise Exposure > Optimal Exposure optimal exposure
- 9. Exposure > Large aperture • Subject is sharp, Background is thrown out of focus
- 10. Exposure > Large aperture ISO: 800 | Aperture: f/5.6 | SS: 1/320 • Subject is sharp • Background is thrown out of focus
- 11. Exposure > Small aperture • At small aperture, both foreground and background are sharp
- 12. Exposure > Small aperture • At small aperture, both foreground and background are sharp
- 13. Exposure > High shutter speed
- 14. Exposure > High shutter speed
- 15. Exposure > Slow shutter speed
- 16. Exposure > Slow shutter speed (Panning)
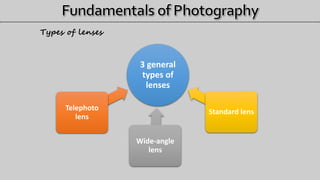
- 17. 3 general types of lenses Telephoto lens Wide-angle lens Standard lens Types of lenses
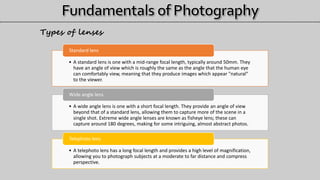
- 18. • A standard lens is one with a mid-range focal length, typically around 50mm. They have an angle of view which is roughly the same as the angle that the human eye can comfortably view, meaning that they produce images which appear "natural" to the viewer. Standard lens • A wide angle lens is one with a short focal length. They provide an angle of view beyond that of a standard lens, allowing them to capture more of the scene in a single shot. Extreme wide angle lenses are known as fisheye lens; these can capture around 180 degrees, making for some intriguing, almost abstract photos. Wide angle lens • A telephoto lens has a long focal length and provides a high level of magnification, allowing you to photograph subjects at a moderate to far distance and compress perspective. Telephoto lens Types of lenses
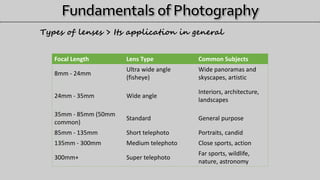
- 19. Types of lenses > Its application in general Focal Length Lens Type Common Subjects 8mm - 24mm Ultra wide angle (fisheye) Wide panoramas and skyscapes, artistic 24mm - 35mm Wide angle Interiors, architecture, landscapes 35mm - 85mm (50mm common) Standard General purpose 85mm - 135mm Short telephoto Portraits, candid 135mm - 300mm Medium telephoto Close sports, action 300mm+ Super telephoto Far sports, wildlife, nature, astronomy
- 20. Wider area is captured by an ultra wide angle lens Types of lenses > Ultra wide angle lens
- 21. Types of lenses > Standard lens Standard lens – no distortion on portraiture
- 22. Types of lenses > Telephoto lens Perspective is compressed when using telephoto lens
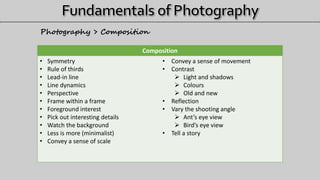
- 23. Composition • Symmetry • Rule of thirds • Lead-in line • Line dynamics • Perspective • Frame within a frame • Foreground interest • Pick out interesting details • Watch the background • Less is more (minimalist) • Convey a sense of scale • Convey a sense of movement • Contrast Light and shadows Colours Old and new • Reflection • Vary the shooting angle Ant’s eye view Bird’s eye view • Tell a story Photography > Composition
- 24. • Symmetry • An image is divided equally into two parts either horizontally or vertically • The simplest form of compositional structure and it helps create a sense of unanimity and harmony • Should only be used for exceptional structures that truly demand such treatment and should be executed in a technically perfect manner Composition > Symmetry
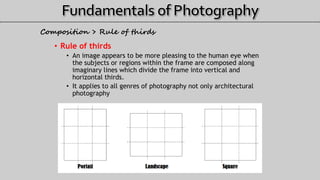
- 26. • Rule of thirds • An image appears to be more pleasing to the human eye when the subjects or regions within the frame are composed along imaginary lines which divide the frame into vertical and horizontal thirds. • It applies to all genres of photography not only architectural photography Composition > Rule of thirds
- 27. Composition > Rule of thirds
- 28. Composition > Rule of thirds
- 29. Composition > Rule of thirds
- 30. Composition > Rule of thirds
- 31. • Lead-in line • Creates the illusion of three-dimensionality • Directs viewer’s eye to the subject • Conveys a sense of depth Composition > Lead-in line
- 32. Composition > Lead-in line
- 33. • Line Dynamics (Diagonal lines) • The art of creating drama to an image and thus attracting the viewer's attention using lines or patterns • Diagonal lines imply a sense of tension, movement, in motion, something dynamic. They upset our sense of perfect balance. Composition > Line Dynamics
- 34. Composition > Line Dynamics
- 35. • Perspective • In short, perspective refers to the relationship of objects in an image — the space between them, their relative size, their placement within the scene. • Becoming more familiar with different perspective styles can be invaluable in your pursuit of creating visually arresting imagery. Composition > Perspective
- 36. Composition > Linear Perspective
- 37. Composition > Height Perspective
- 38. Composition > Atmospheric/Aerial Perspective
- 39. • Frame within a frame • Can add depth and context • Drawing viewer’s attention to a defined subject • Enhance the illusion of three-dimensionality Composition > Frame within a frame
- 40. Composition > Frame within a frame
- 41. Composition > Frame within a frame
- 42. Composition > Foreground interest • Foreground interest • Creates the illusion of three-dimensionality • Directs viewer’s eye to the subject • Conveys a sense of depth
- 43. Composition > Foreground interest
- 44. Composition > Pick out interesting details • Pick out interesting details • Zoom in on details which can result in an arresting image out of ordinary things around us
- 45. Composition > Pick out interesting details
- 46. Composition > Watch the background • Watch the background • Avoid a cluttered background to make your subject stand out
- 47. Composition > Watch the background
- 48. Composition > Less is more • Less is more • Negative space - the areas of an image, lacking in detail, or empty space, is a common and overwhelming element in minimalism. This can be used to provoke a strong compulsion toward the main subject of the photograph by setting the subject in isolation.
- 49. Composition > Less is more
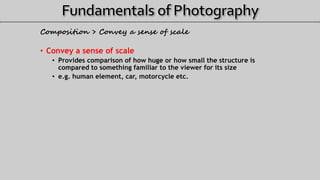
- 50. Composition > Convey a sense of scale • Convey a sense of scale • Provides comparison of how huge or how small the structure is compared to something familiar to the viewer for its size • e.g. human element, car, motorcycle etc.
- 51. Composition > A sense of scale
- 52. Composition > A sense of scale
- 53. Composition > Convey a sense of movement • Convey a sense of movement • A still photo is something static. By introducing motion into a photo it shows movement and this produces a dynamic image
- 54. Composition > Convey a sense of movement
- 55. Composition > Contrast • Contrast Contrast is a broad term, and can be interpreted in several ways. You can use any of these interpretations for more creative photography. Let’s look at some of the ways contrast can be applied • Light and shadows - The most obvious when it comes to photography is to use the light in your photo. You can use this to accentuate areas of interest on the subject, by using shadows to show detail points. • Colours – In some cases, you can play colors off against each other. You need to be creative about how you add opposite colors that contrast with it. • Old and new – Old architecture surrounded by new can make an effective photo. Think of a church or temple surrounded by modern skyscrapers.
- 56. Composition > Contrast > Light & shadow
- 57. Composition > Contrast > Colours
- 58. Composition > Contrast > Old and new
- 59. Composition > Reflection • Reflections • Reflections can be used to instill a degree of atmosphere in an image. And the reflections balance the image to give a composition that’s pleasing to the eye. • Slow shutter speed serves to ‘smooth’ out the rough water and gives the impression of a calmer scene than it actually is • For sharpest reflections in the water, calm weather conditions are a must and higher shutter speed will freeze any movement of the water. Even a slight wind can be enough to pick up a few ripples and disturb the reflections.
- 61. Composition > Vary the shooting angle • Vary the shooting angle • Ant’s eye view - Unusual perspectives impact the experience of the viewer or audience too. From the low perspective, the ground and the horizon either intersect or sandwich the subject material, creating emphasis and guiding the eye around the image. When these planes come together abruptly, they also draw attention to the composition of the environment. By enhancing the depth of the image, the image appeals to the human eye because it is both familiar and unusual at the same time. • Bird’s eye view - This angle or perspective finds great use in film making as many film makers use this view to click and record shots. The view turns out to be amazing in most cases and helps to lend variations to the way the central character is captured. Bird’s eye view is great for clicking pictures of cities for travel magazines and shows. These pictures prove useful for postcards, newspapers and for brochures. Many photographers’ find bird’s eye view very interesting and use only this perspective for their collections. It is a perspective different from many others and is hence considered valued in the field of photography. It is often difficult to take and requires a lot of skill and patience. This is another reason why bird eye view photographs are considered good.
- 62. Composition > Vary the shooting angle
- 63. Composition > Vary the shooting angle
- 64. Composition > Tell a story • Tell a story • A good picture is usually able to tell a story • After all as they said a picture is worth a thousand words • Story can be told by either a single photograph or a series of photographs • This skill is especially vital in photojournalism and documentary photography where a single photo is able to tell a dramatic story
- 65. Composition > Tell a story
- 66. Composition > Tell a story
- 67. Composition > Tell a story
- 68. Composition > Tell a story
- 69. Lighting • Ideal time to take photo is in the early morning and late evening • It results in soft warm light but pronounced three- dimensionality • Beautiful contrasty scene • Works best for landscape, travel and architecture • It is called the magic hour especially one hour after sunrise and one hour before sunset Lighting
- 70. • Side lighting • If the building faces either North or South, side lighting is the only choice depending on what time the sun light hits the facade. • Front lighting • It depends which direction the building faces – east or west • Silhouette results during sunrise or sunset depends which direction the subject is facing • Night shooting Lighting > Types of lighting
- 71. Lighting > Late evening light > Side lighting
- 72. Lighting > Late evening light > Side lighting
- 73. Lighting > Early morning light > Side lighting
- 74. Lighting > Early morning light > Front lighting
- 75. Lighting > Late evening light > Front lighting
- 76. Lighting > Silhouette > Sunset
- 79. Lighting > Night shooting Night shooting: Shoot during early night when the skies still retain some colours
- 80. Types of Photography 15 Top Photography Genres that you need to know 1. Aerial photography 9. Photojournalism 2. Architectural photography 10. Conceptual/fine art photography 3. Candid photography 11. Portraiture photography 4. Documentary photography 12. Sports photography 5. Fashion photography 13. Street photography 6. Food photography 14. War photography 7. Landscape photography 15. Wildlife photography 8. Night-long exposure photography
- 81. What makes a good photograph? • It is a fundamental skill to master as a photographer Composition • Deep understanding of light is needed Light • The timing, depending on the type of photography you do, can be a matter of capturing that instant of a second that makes a difference. You have to capture a moment – the magic moment Timing • Closely related to timing. A photo is worth a thousand words The story • An essential skill in digital photography Image processing • Show clearly what you want to present and a good photographer is able to visualize the picture even before the photo is captured Have a clear vision/reason
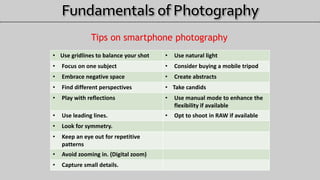
- 82. Tips on smartphone photography • Use gridlines to balance your shot • Use natural light • Focus on one subject • Consider buying a mobile tripod • Embrace negative space • Create abstracts • Find different perspectives • Take candids • Play with reflections • Use manual mode to enhance the flexibility if available • Use leading lines. • Opt to shoot in RAW if available • Look for symmetry. • Keep an eye out for repetitive patterns • Avoid zooming in. (Digital zoom) • Capture small details.
- 83. Shot with Huawei Mate 10
- 84. Shot with Huawei Mate 10
- 85. Shot with Huawei Mate 10
- 86. Shot with Huawei Mate 10
- 87. “If your pictures aren’t good enough, you’re not close enough.” – Robert Capa “Which of my photographs is my favorite? The one I’m going to take tomorrow.” – Imogen Cunningham "Photography has not changed since its origin except in its technical aspects, which for me are not important". - Henri Cartier-Bresson “The whole point of taking pictures is so that you don’t have to explain things with words.” – Elliott Erwitt “Every building is a snapshot of a particular time and place - the raw materials that were on hand, how far the builders' technology had progressed, and the aspirations of its creators. But architecture also makes a powerful statement about the unique culture it reflects, whether the elegant simplicity of a grass bungalow, or the dramatic complexity of a chrome skyscraper. One whispers, the other shouts, but both are enduring reminders of cultural identity.” -- Todd Gipstein