Business models overview
- 1. Business Models Primer INNOVATION PRIMER INTRO TO BIZ MODELS
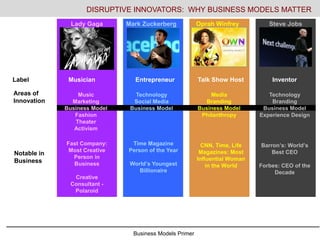
- 2. Business Models Primer DISRUPTIVE INNOVATORS: WHY BUSINESS MODELS MATTER Lady Gaga Mark Zuckerberg Oprah Winfrey Steve Jobs Label Musician Entrepreneur Talk Show Host Inventor Areas of Innovation Notable in Business Fast Company: Most Creative Person in Business Creative Consultant - Polaroid Time Magazine Person of the Year World’s Youngest Billionaire Barron’s: World’s Best CEO Forbes: CEO of the Decade CNN, Time, Life Magazines: Most Influential Woman in the World Music Marketing Business Model Fashion Theater Activism Technology Social Media Business Model Media Branding Business Model Philanthropy Technology Branding Business Model Experience Design
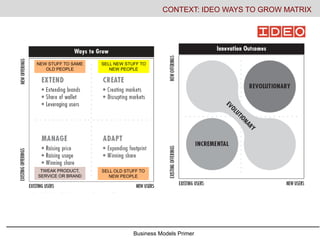
- 3. Business Models Primer CONTEXT: IDEO WAYS TO GROW MATRIX NEW STUFF TO SAME OLD PEOPLE TWEAK PRODUCT, SERVICE OR BRAND SELL OLD STUFF TO NEW PEOPLE SELL NEW STUFF TO NEW PEOPLE
- 4. Business Models Primer WHAT IS INNOVATION? EXAMPLES OF DISRUPTIVE INNOVATION
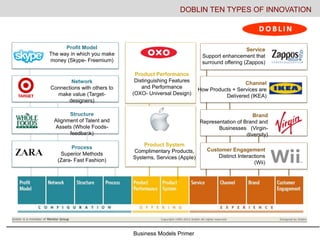
- 5. Business Models Primer Profit Model The way in which you make money (Skype- Freemium) Network Connections with others to make value (Target- designers) Structure Alignment of Talent and Assets (Whole Foods- feedback) Process Superior Methods (Zara- Fast Fashion) Product Performance Distinguishing Features and Performance (OXO- Universal Design) Product System Complimentary Products, Systems, Services (Apple) Service Support enhancement that surround offering (Zappos) Channel How Products + Services are Delivered (IKEA) Brand Representation of Brand and Businesses (Virgin- diversity) Customer Engagement Distinct Interactions (Wii) DOBLIN TEN TYPES OF INNOVATION
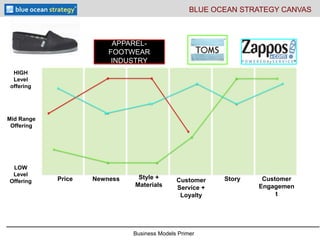
- 6. Business Models Primer APPAREL- FOOTWEAR INDUSTRY Price Newness Style + Materials Story Customer Engagemen t LOW Level Offering HIGH Level offering Customer Service + Loyalty Mid Range Offering BLUE OCEAN STRATEGY CANVAS
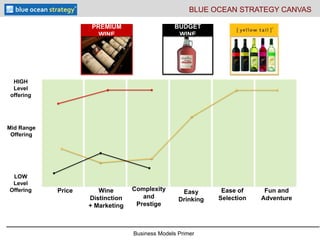
- 7. Business Models Primer Price Wine Distinction + Marketing Complexity and Prestige Ease of Selection Fun and Adventure Easy Drinking BUDGET WINE PREMIUM WINE BLUE OCEAN STRATEGY CANVAS LOW Level Offering HIGH Level offering Mid Range Offering
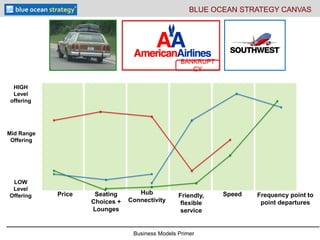
- 8. Business Models Primer Price Seating Choices + Lounges Hub Connectivity Speed Frequency point to point departures Friendly, flexible service BANKRUPT CY BLUE OCEAN STRATEGY CANVAS LOW Level Offering HIGH Level offering Mid Range Offering
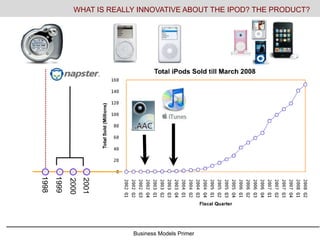
- 9. Business Models Primer WHAT IS REALLY INNOVATIVE ABOUT THE IPOD? THE PRODUCT?
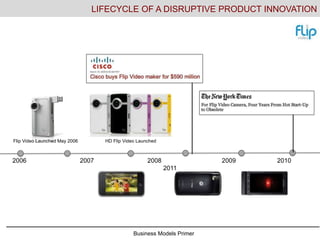
- 10. Business Models Primer 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 LIFECYCLE OF A DISRUPTIVE PRODUCT INNOVATION Flip Video Launched May 2006 HD Flip Video Launched
- 11. Business Models Primer WHAT EXACTLY IS A BUSINESS MODEL?
- 12. Business Models Primer BUSINESS MODEL= ENGINE FINANCIAL MODEL= FUEL OR ENERGY BUSINESS PLAN= ROAD OR TRIP PLAN BUSINESS MODELS: RELATED BUT OFTEN CONFUSED
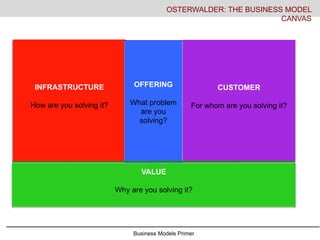
- 13. Business Models Primer Key Activities Key Resources Key Partners INFRASTRUCTURE How are you solving it? The Value Proposition Solution to the Pain Point OFFERING What problem are you solving? Customer Relationship s Distribution Channels Customer Segments CUSTOMER For whom are you solving it? Cost Structure Revenue Streams VALUE Why are you solving it? OSTERWALDER: THE BUSINESS MODEL CANVAS
- 14. Business Models Primer $1000 per year $400-500 per year (device cost $250-$700) Educational Textbooks
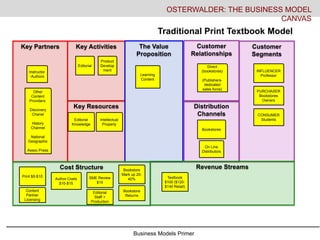
- 15. Business Models Primer Key Activities Key Resources Key Partners The Value Proposition Customer Relationships Distribution Channels Customer Segments Cost Structure Revenue Streams OSTERWALDER: THE BUSINESS MODEL CANVAS Traditional Print Textbook Model Instructor -Authors Editorial Product Develop ment Learning Content Direct (bookstores) (Publishers- dedicated sales force) On Line Distributors Bookstores CONSUMER Students PURCHASER Bookstores Owners INFLUENCER Professor Editorial Knowledge Other Content Providers: Discovery Chanel History Channel National Geographic Assoc Press Intellectual Property Print $5-$10 Author Costs $10-$15 SME Review $15 Bookstore Mark up 20- 40% Bookstore Returns Editorial Staff + Production Textbook $100 ($120- $140 Retail) Content Partner Licensing
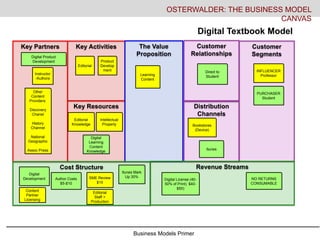
- 16. Business Models Primer Key Activities Key Resources Key Partners The Value Proposition Customer Relationships Distribution Channels Customer Segments Cost Structure Revenue Streams OSTERWALDER: THE BUSINESS MODEL CANVAS Digital Textbook Model Instructor -Authors Editorial Product Develop ment Learning Content Direct to Student Itunes Bookstores (Device) PURCHASER Student INFLUENCER Professor Editorial Knowledge Other Content Providers: Discovery Chanel History Channel National Geographic Assoc Press Intellectual Property Digital Development Author Costs $5-$10 SME Review $15 Itunes Mark Up 30% NO RETURNS CONSUMABLE Editorial Staff + Production Digital License (40- 50% of Print). $40- $50) Content Partner Licensing Digital Product Development Digital Learning Content Knowledge
- 17. Business Models Primer Home Video/Movies $2.99 plus late fees $4.99-$19.99 month $7.99 month unlimited streaming $7.99 additional DVD mail unlimited $1 per night To Be Determined
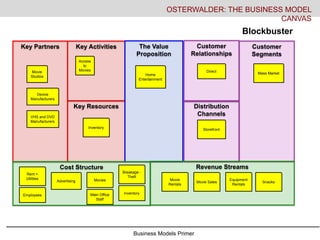
- 18. Business Models Primer Key Activities Key Resources Key Partners The Value Proposition Customer Relationships Distribution Channels Customer Segments Cost Structure Revenue Streams OSTERWALDER: THE BUSINESS MODEL CANVAS Blockbuster Movie Studios Access to Movies Home Entertainment Direct Storefront Mass Market Inventory Rent + Utilities Advertising Movies Breakage - Theft InventoryMain Office Staff Movie Rentals Employees Device Manufacturers VHS and DVD Manufacturers Movie Sales Equipment Rentals Snacks
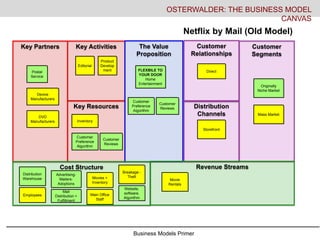
- 19. Business Models Primer Key Activities Key Resources Key Partners The Value Proposition Customer Relationships Distribution Channels Customer Segments Cost Structure Revenue Streams OSTERWALDER: THE BUSINESS MODEL CANVAS Netflix by Mail (Old Model) Postal Service Editorial Product Develop ment FLEXBILE TO YOUR DOOR Home Entertainment Direct Storefront Originally Niche Market Inventory Distribution Warehouse Advertising- Mailers- Adoptions Movies + Inventory Breakage - Theft Website, software, Algorithm Main Office Staff Movie Rentals Employees Device Manufacturers DVD Manufacturers Customer Preference Algorithm Customer Reviews Mass Market Mail Distribution + Fulfillment Customer Preference Algorithm Customer Reviews
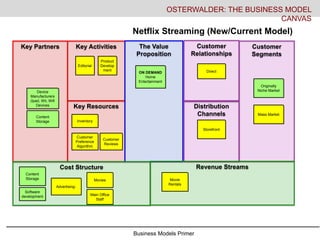
- 20. Business Models Primer Key Activities Key Resources Key Partners The Value Proposition Customer Relationships Distribution Channels Customer Segments Cost Structure Revenue Streams OSTERWALDER: THE BUSINESS MODEL CANVAS Netflix Streaming (New/Current Model) Editorial Product Develop ment ON DEMAND Home Entertainment Direct Storefront Originally Niche Market Inventory Content Storage Advertising- Movies Main Office Staff Movie Rentals Device Manufacturers (Ipad, Wii, Wifi Devices Content Storage Customer Preference Algorithm Customer Reviews Mass Market Software development
- 21. Business Models Primer What have we learned: Innovation is more than product development and inventions Business Models, Business Plans and Financial Models are different yet related and integrated. External factors- changes in the environment force (and afford) business model innovation. Industry disruption requires an integration of product/service innovation, infrastructure, and business.
Editor's Notes
- #3: All of these ‘innovators’ with whom you should be familiar have been hugely successful by making dramatic changes to their industry. Notably they all have created some form of business model innovation
- #4: This is referred to as the Ansoff model, later adopted by IDEO as the ways to grow model. The basics of the model if you start with the lower right, in simple terms if you can sell more of the same stuff or raise the price of your existing offerings to your existing customers, you can sell your existing offerings to new customers/markets, you can sell new stuff your existing customers or markets or you can sell new stuff to new people– new products new markets- blue oceans
- #6: The ten types of innovation are offered to illustrate that innovation is a spectrum. The Doblin Group, the consulting firm that came up with this framework did a study and found that more than 50% of resources are focused on product and offering innovation (new products, new features) but most fail. Greater financial returns can be found other areas such as configuration- networking, structure, and process as well as in service design, customer engagement and channel. We are going to work today at uncovering opportunities that may be in new product ideas but may also be beyond the offering.
- #7: Examples of Blue Oceans and disruptive innovation: Blue Ocean has a number of examples we can use. They have tools on their website and video cases, PPT etc that we can use for free as educators. I have been in touch with them to discuss what we are doing. This is their strategy canvas which is used to really look at the customer value proposition. Companies compete The apparel industry competes on price (either exclusively high or discounting), newness of offering and style, materials and brand (AKA design). Two examples of industry- business model disruptors are Tom’s shoes and Zappos. Both of which students should be familiar with. Tom’s is about the story and customer engagement. They make crappy cheap shoes from a design 100+ years old from a third world country out of old, inexpensive materials. Their story is for every pair of shoes you buy, they give away a pair to child in need in a country like africa or south america. They don’t advertise, their customers are evangelical about the brand and the story. They have created awareness events such as no shoe day to raise consciousness about how the bottom of the pyramid lives without shoes. Zappos sells product not unique to departments and specialty stores. They rarely discount- so they don’t really compete on price or newness but they have outstanding customer service- you can buy 10 pairs of shoes, have them shipped next day for free and return all 10 pays 365 days later. Most people don’t but they buy the story. They have live customer agents who are carefully screened. They frame their offering as customer service not shoes- they sell happiness.
- #8: The wine industry- largely runs on insecurity. The industry has a high degree of complexity such that people buy on price “this more expensive bottle must be better” or they buy volume. Yellow tail discovered this turned a large pool of potential customers off and into other beverages so they create a wine that is simple to understand, simple to buy, easy to drink, and priced at a mid level so you don’t feel like you are buying cheap rot gut. It doesn’t intimidate you, it doesn’t embarrass you. It has become the best selling wine in north america by volume in a very short period of time by finding a place in converting non customers to the traditional wine market. They sell more wine in the US market then all french imports combined.
- #9: The airline industry had seen itself as strickly competing with other carriers- high fixed costs, hub costs, and pricing that resulted in low plane utilization (half full flights). Customers experienced hub connections, transfers, high costs, and inflexible changes. Southwest saw itself in the transportation industry- competing with both cars and trains. They looked at smaller connections between regional jumps where their competition was established shuttle flights (high cost), train travel (medium cost, longer travel time) and car travel (low cost, flexible travel, longer travel time). They offered low cost (often lower than gas prices for car travel) between points that would compete with car/train travel based on distance (4-6 hour travel time) and built an offering with low cost, highly flexible purchases to frequently traveled routes, they pack the planes, stream lined the boarding, deboarding and turn around time to reduce the lost time on the ground and increase travel time into the most profitable airline.
- #10: This is rarely understood. Apple was not the first MP3. The Rio came first, Napster came next. Napster was the file sharing program that shut down digital content as the music industry was bleeding. Apple worked with the music industry to develop a standard of copyright protection for digital music. Then Apple created a market place (itunes) for purchase and organization of music. This is when the rapid growth of units and offerings began
- #11: This example is shown to drive home the importance of studying this type of dynamic thinking about business. The Flip camera was introduced, disrupted the market, was acquired at a very high premium, and was discontinued in a period of time equivalent to an undergrad education. What is going to change while you are studying? Life long learning! Smart phones increased the resolution and capabilities to capture, edit, and upload video essentially making an extra device, which required extra steps (computer upload, editing, etc) unnecessary when you have your video camera in your phone and in your pocket.
- #13: The business model, business plan, and financial model are often confused and often used interchangeably which they are not. They are all important and all related but not the same. The car is used her as an example- the business model is like the engine- it makes the car work. The business model requires fuel or the engine doesn’t work. The financial model is the fuel or energy that makes it go. The business plan is like steering or driving= where you are going. You can’t drive without and engine or without gas/fuel. So we begin with the business model
- #14: The business model canvas is offered as a nice framework for looking at how the company functions. There are 9 basic building blocks for a business model which we will go into in a moment but first, lets look at the four basic clusters which aligns a bit with the DEC core In IDP you worked on understanding the offering. What problem are you trying to solve. You worked on finding problems/opportunities. Then you have to look at for whom are you solving the problem- your customers. In ethnographic research methods you will deeply study people which to some extent will help you understand customers. Students who study marketing or have additional courses in marketing or consumer insights will make deeper study here as well. Infrastructure is how you solve the problem- what resources, activities, and partners you rely on to deliver value. To some extent in system thinking you will look at different types of infrastructure, complexity and consequences Value is why are you solving this problem- how does it deliver value to you and others. IN this business model course we will look at value creation- traditionally the value portion of the canvas looks at costs and revenue but we will look at other types of value- social, political, environmental, etc
- #15: This is something you should all be familiar with. The changing dynamics in educational content delivery at the university level. The average a student in the US pays at undergrad for book is about $1000. The publishers who supply this material are working with partners such as apple and are trying to create the same or better educational content offerings at half the price. This requires the purchase of a device initially so you first year costs are the same but then drop in half in follow on years. All this and no broken back for 50lbs of paper We will now walk through two business models in the same industry side by side
- #16: This is offered as an example of the traditional existing print textbook model. As an example here we use the $120-$140 big textbook you buy at the bookstore. The publisher sells into the book store for $100- pays authors about $10-15, pays $5-$10 to get it printed, pays about $15 to subject matter experts in reviewing the product and related content development, it goes through internal editors, and then out through the publishers sales force to the professors who adopt the book then sold by the bookstores. With increasing demand for dynamic content, publishers include CDs, links to websites with passwords etc through which they offers supplementary content from their partnerships with History Channel, discovery channel, associated press, etc. As students increasing buy used textbooks, share books, even look at renting books this model is under pressure.
- #17: The digital model changes some factors but not all. The yellow are factors that remain, offerings, costs etc. The pricing changes- the device cost becomes a large upfront fixed cost which may change with a leasing model or the like. Content is now sold through itunes as opposed to the bookstore with margins about the same (30%), The publishers partner with external partners for digital product development, they are trying to cut authors royalties in half with the argument that volume should go up as digital becomes a consumable (no returns, can’t sell used PDFs like used books if digital rights are secure), The ultimate value proposition to the customer/student is much better in the long haul but the publishers must realign their internal costs to compete. There are certainly other ways to disrupt the model, cutting out the publishers all together with models of author co-creation and building content directly for ipads but this example is just to look from a publishers view at two models side by side that are current today.
- #18: The home entertainment industry is amidst rapid change. Not long ago Blockbuster owned the space. You paid $3 and got a new release if they had it, you paid late fees and you had to drive to the store to get it. Netflix figured out a model of DVDs by mail with a fixed lower cost and no late fees. Shortly after that and in parrallel Netflix launched a streaming option with an all you can consume of digital content (although options more limited) for $8 a month. Red Box has come forward with a lower objection, new release impulse option to pick a DVD for $1 at the grocery store or mall with a focus on new releases. Red Box and Verizon launched a partnership with Verizon which might be fun to contrast if the details become available about that this spring or summer. For now we will focus on Blockbuster vs. Netflix DVD by Mail vs. Netflix streaming as three models with which students should be familiar
- #19: Blockbuster came out and replaced the mom and pop video stores with a focus on new releases. Blockbuster would get a huge inventory of a newly released movie and most of its business was in the first 60 days of a release. After that product moved to the middle of the store where they had very low turns. The business is mass market, direct to customer, distributed through a storefront. Their key partners were movie studios for content, DVD and VHS producers, and equipment providers. The video business wouldn’t work without affording home video players- a key partnership- just like the light bulb wouldn’t work without the electric company. Key activity is access to movies, key resource is their inventory- particularly of new content. Cost structure was high and fixed- rent and utilities, employees, advertising, inventory, corporate office or franchise fee to corporate office, breakage/theft and the cost of acquiring movies. There revenue diversified later in the game to include game rentals, equipment rentals, movie sales and crappy snacks but it was initially based on the $2.99 movie rental.
- #20: Now we look at the Netflix by mail option in contrast to blockbuster. The value proposition increased by the flexibility of the product delivered right to your door with no late fees. Netflix also created a substantial customer review database and a proprietary algorithm that could predict what type of movies you like based upon an initial questionnaire and rental patterns. This allowed them to shift the focus away from their higher cost new releases to move their backlist- that center section of the store that blockbuster could never turn became then a big piece of the netflix business. Their key partners were the device manufactures- DVD players, DVD manufacturers and then the post office. The post office is a big piece of their infrastructure. Their cost structure shifted from fix storefront costs to distribution center costs, fulfillment etc. They had increased advertising costs for that initial customer acquisition. They moved from a per piece revenue/rental to a fixed month subscriber stream.
- #21: Here we look in contrast at Netflix by mail vs. Netflix streaming. Netflix runs these business models in tandem. T The streaming model adds on demand to the value proposition as you can start watching the moment you decided you want to see a movie/tv show. No trip to the store, no wait for the mail. It requires partnership with new device manufacturers- laptops, ipads, smart phones, wii/gaming consoles, set top boxes like tivo, apple tv and roku. It requires content storage for streaming, software development to optimize streaming, wifi providers to supply the wireless infrastructure. Many of these factors are costs such as storage and software development as well as the cost of licensing the movie for rental, and the revenue remains the subscription service.
- #22: Summary Innovation is more than product development and inventions Business Models, Business Plans and Financial Models are different yet related and integrated. Technological, behavioral (knowledge and comfort adopting technology), financial, and other factors influence changes to business models. Industry disruption requires an integration of product/service innovation, infrastructure, and commerce. This course focuses on the business model but offers an integrated view of the DEC core through understanding that IDP introduced you to finding problems and opportunities, ethnographic research methods will increase your understanding of people which is key to understand customers, their needs and motivation and systems thinking will introduce to you complexity and consequences factors that often are inherent in understanding how to optimize your infrastructure. This course while showing you an overview of the business model and how it works together will also introduce you to value creation in cost and revenue terms- financial, social, political, and environmental