Animal Kingdom
- 1. T- 1-855-694-8886 Email- info@iTutor.com By iTutor.com
- 2. What is an animal? Kingdom Animalia divided into two major groups: – invertebrates – vertebrates Worm Snail Cockroach An invertebrate is an animal without a backbone. About 98 percent of all animals are invertebrates. Invertebrate
- 3. Vertebrates Only about two percent of all animals are vertebrates which belong to the Phylum Chordata. Vertebrates include fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. BirdFrog Rat Animals share the following characteristics: 1. Animals are multi cellular and have eukaryotic cells. 2. Animal cells lack cell walls. 3. Animals have a period of embryonic development. 4. Animals are consumers. 5. Animals can move. 6. Most animals have muscle and nervous tissue. 7. Animals are diploid.
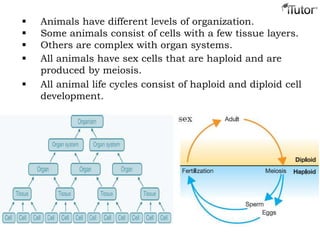
- 4. Animals have different levels of organization. Some animals consist of cells with a few tissue layers. Others are complex with organ systems. All animals have sex cells that are haploid and are produced by meiosis. All animal life cycles consist of haploid and diploid cell development.
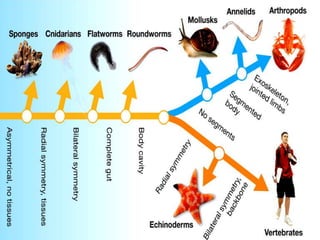
- 5. Animal body plan and Symmetry The arrangement of an animal’s body parts is called its symmetry. Animals that do not have an orderly body plan, like sponges, are called asymmetrical. Radial symmetry means that the body parts are arranged in a circle around a central point. In bilateral symmetry, the body consists of two similar halves.
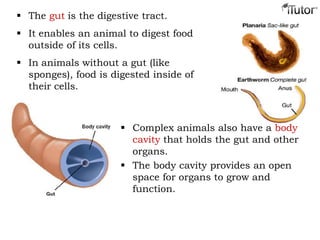
- 6. The gut is the digestive tract. It enables an animal to digest food outside of its cells. In animals without a gut (like sponges), food is digested inside of their cells. Complex animals also have a body cavity that holds the gut and other organs. The body cavity provides an open space for organs to grow and function.
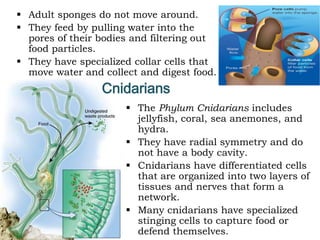
- 7. As animals evolved and became more complex, they developed organ systems to perform basic functions. Organ Systems Some important organ systems are: – Skeletal – Muscular – Circulatory – Digestive – Nervous – Reproductive Sponges belong to the Phylum Porifera (“pore bearing.”) They are asymmetrical and do not have a body cavity. Sponges
- 8. Adult sponges do not move around. They feed by pulling water into the pores of their bodies and filtering out food particles. They have specialized collar cells that move water and collect and digest food. Cnidarians The Phylum Cnidarians includes jellyfish, coral, sea anemones, and hydra. They have radial symmetry and do not have a body cavity. Cnidarians have differentiated cells that are organized into two layers of tissues and nerves that form a network. Many cnidarians have specialized stinging cells to capture food or defend themselves.
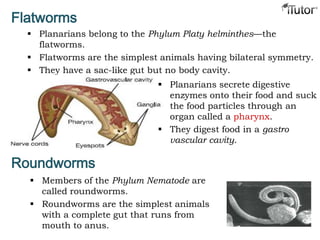
- 9. Flatworms Planarians belong to the Phylum Platy helminthes—the flatworms. Flatworms are the simplest animals having bilateral symmetry. They have a sac-like gut but no body cavity. Planarians secrete digestive enzymes onto their food and suck the food particles through an organ called a pharynx. They digest food in a gastro vascular cavity. Roundworms Members of the Phylum Nematode are called roundworms. Roundworms are the simplest animals with a complete gut that runs from mouth to anus.
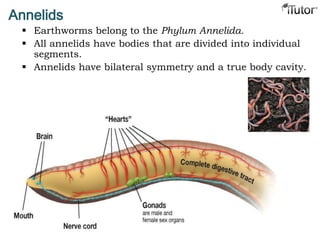
- 10. Annelids Earthworms belong to the Phylum Annelida. All annelids have bodies that are divided into individual segments. Annelids have bilateral symmetry and a true body cavity.
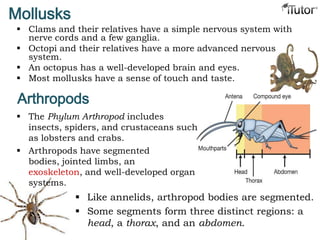
- 11. Mollusks Snails, clams, and squids are all members of the Phylum Mollusca. Mollusks have bilateral symmetry and a true body cavity. The body of a mollusk typically has a foot, gut, mantle, and shell. Body of a mollusk
- 12. Mollusks Clams and their relatives have a simple nervous system with nerve cords and a few ganglia. Octopi and their relatives have a more advanced nervous system. An octopus has a well-developed brain and eyes. Most mollusks have a sense of touch and taste. Arthropods The Phylum Arthropod includes insects, spiders, and crustaceans such as lobsters and crabs. Arthropods have segmented bodies, jointed limbs, an exoskeleton, and well-developed organ systems. Like annelids, arthropod bodies are segmented. Some segments form three distinct regions: a head, a thorax, and an abdomen.
- 13. Echinoderms The Phylum Echinodermata (meaning “spiny skin”) includes starfish, sea urchins, and sea cucumbers. Echinoderms have radial symmetry, a body cavity, an internal skeleton, and spiny skin. Echinoderms have a specialized water vascular system. The water vascular system is a network of fluid-filled canals connected to hundreds of tiny, tube-like feet. The water vascular system helps them move and capture food.
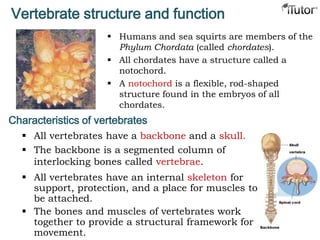
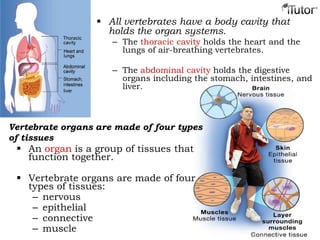
- 15. Vertebrate structure and function Humans and sea squirts are members of the Phylum Chordata (called chordates). All chordates have a structure called a notochord. A notochord is a flexible, rod-shaped structure found in the embryos of all chordates. Characteristics of vertebrates All vertebrates have a backbone and a skull. The backbone is a segmented column of interlocking bones called vertebrae. All vertebrates have an internal skeleton for support, protection, and a place for muscles to be attached. The bones and muscles of vertebrates work together to provide a structural framework for movement.
- 16. All vertebrates have a body cavity that holds the organ systems. – The thoracic cavity holds the heart and the lungs of air-breathing vertebrates. – The abdominal cavity holds the digestive organs including the stomach, intestines, and liver. Vertebrate organs are made of four types of tissues An organ is a group of tissues that function together. Vertebrate organs are made of four types of tissues: – nervous – epithelial – connective – muscle
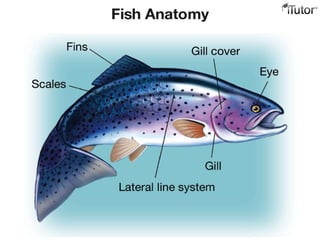
- 17. Fish Fish are exothermic, aquatic vertebrates with fins, gills, and a streamlined body. They were the first vertebrates, and evolved about 500 million years ago. There are three classes of fish living today. – jawless fish – cartilaginous fish – bony fish
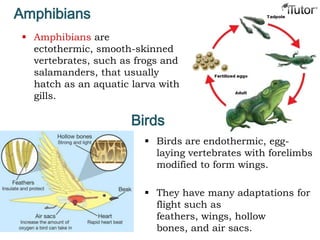
- 19. Amphibians Amphibians are ectothermic, smooth-skinned vertebrates, such as frogs and salamanders, that usually hatch as an aquatic larva with gills. Birds Birds are endothermic, egg- laying vertebrates with forelimbs modified to form wings. They have many adaptations for flight such as feathers, wings, hollow bones, and air sacs.
- 20. Mammals are endothermic vertebrates that have mammary glands. Mammary glands are organs that produce a nutritious fluid called milk. Mammals Mammals evolved from a now-extinct group of reptiles called therapsids. The earliest true mammals appeared over 200 million years ago.
- 21. The end Call us for more Information: www.iTutor.com 1-855-694-8886 Visit