advancepresentationskillshdhdhhdhdhdhhfhf
- 2. OBJECTIVES: 01 02 03 04 *Definition *Excel Layouts/Interfaces *Describe terms, views, and functions of Microsoft PowerPoint *Application of PowerPoint Define Presentation Tool Different Presentation Tools Application MS PowerPoint Discuss tips on how to make effective presentations 05 Define Hyperlink * Functions and Processes of Hyperlink 06 Embedding Files and Data
- 4. WHAT IS PRESENTATION TOOL? Presentation tools are digital applications designed to create and deliver visual presentations using text, graphics, audio, and video. They help users capture audience attention, improve communication, and visualize ideas effectively.
- 5. Slide-based design Content formatting Users can add, edit, and style text, images, charts, and other visual elements. Most tools allow users to organize infromation into slides, similar to pages in a notebook. Multimedia integration Features include adding audio, video, and animations to enhance engagement. 4 KEY FUNCTIONS: Collaborative features Tools often enable real-time teamwork and feedback sharing.
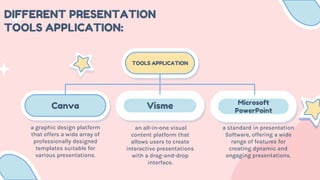
- 7. Canva Visme Microsoft PowerPoint DIFFERENT PRESENTATION TOOLS APPLICATION: TOOLS APPLICATION a graphic design platform that offers a wide array of professionally designed templates suitable for various presentations. an all-in-one visual content platform that allows users to create interactive presentations with a drag-and-drop interface. a standard in presentation Software, offering a wide range of features for creating dynamic and engaging presentations.
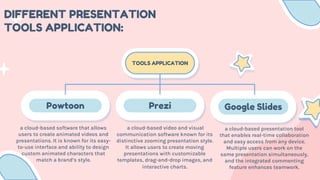
- 8. Powtoon Prezi Google Slides DIFFERENT PRESENTATION TOOLS APPLICATION: TOOLS APPLICATION a cloud-based software that allows users to create animated videos and presentations. It is known for its easy- to-use interface and ability to design custom animated characters that match a brand’s style. a cloud-based video and visual communication software known for its distinctive zooming presentation style. It allows users to create moving presentations with customizable templates, drag-and-drop images, and interactive charts. a cloud-based presentation tool that enables real-time collaboration and easy access from any device. Multiple users can work on the same presentation simultaneously, and the integrated commenting feature enhances teamwork.
- 10. - Is a presentation program designed to create slideshows with text, graphics, and other multimedia elements. It is a tool used for visual demonstrations in various settings, including business, education, and, and community organizations. - Originally created by Robert Gaskins and Dennis Austin at Forethought, Inc., it was initially named “Presenter” and launched for Apple Macintosh in 1987. I. MICROSOFT POWERPOINT
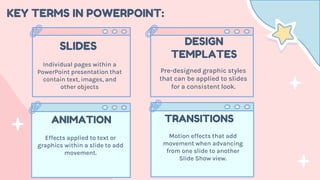
- 11. KEY TERMS IN POWERPOINT: Individual pages within a PowerPoint presentation that contain text, images, and other objects Pre-designed graphic styles that can be applied to slides for a consistent look. SLIDES DESIGN TEMPLATES ANIMATION Effects applied to text or graphics within a slide to add movement. TRANSITIONS Motion effects that add movement when advancing from one slide to another Slide Show view.
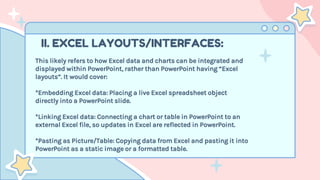
- 12. II. EXCEL LAYOUTS/INTERFACES: This likely refers to how Excel data and charts can be integrated and displayed within PowerPoint, rather than PowerPoint having “Excel layouts”. It would cover: *Embedding Excel data: Placing a live Excel spreadsheet object directly into a PowerPoint slide. *Linking Excel data: Connecting a chart or table in PowerPoint to an external Excel file, so updates in Excel are reflected in PowerPoint. *Pasting as Picture/Table: Copying data from Excel and pasting it into PowerPoint as a static image or a formatted table.
- 13. III. PowerPoint Terms, Views and Functions PowerPoint offers various views for different stages of presentation creation and delivery. These views can be accessed from the View tab on the ribbon or the task bar at the bottom right of the slide window.
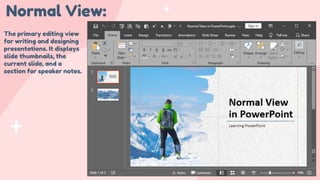
- 14. Normal View: The primary editing view for writing and designing presentations. It displays slide thumbnails, the current slide, and a section for speaker notes.
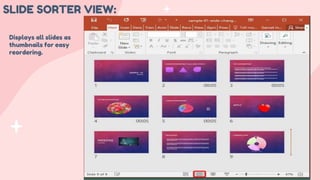
- 15. SLIDE SORTER VIEW: Displays all slides as thumbnails for easy reordering.
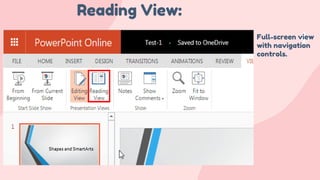
- 16. Reading View: Full-screen view with navigation controls.
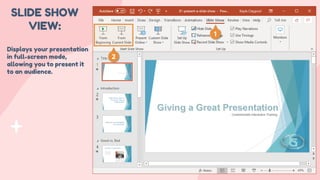
- 17. SLIDE SHOW VIEW: Displays your presentation in full-screen mode, allowing you to present it to an audience.
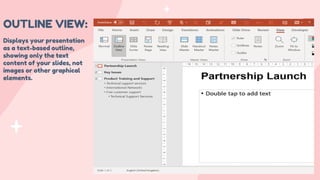
- 18. OUTLINE VIEW: Displays your presentation as a text-based outline, showing only the text content of your slides, not images or other graphical elements.
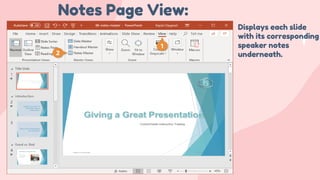
- 19. Notes Page View: Displays each slide with its corresponding speaker notes underneath.
- 20. IV. APPLICATION OF POWERPOINT Business – Sales pitches, marketing presentations, quarterly reports, training modules. Education – Lectures, student projects, research presentations. Personal – Photo albums, event invitations, family histories. General Communication – Conveying complex information clearly and visually..
- 21. 04 DISCUSS TIPS ON HOW TO MAKE EFFECTIVE PRESENTATIONS
- 22. TIPS ON HOW TO MAKE EFFECTIVE PRESENTATIONS: This section focuses on best practices for creating compelling and impactful presentations, regardless of the tool used. To deliver effective presentations, focus on engaging the audience, structuring your content clearly, and utilizing visual aids effectively.
- 23. KEY TIPS: Tailor content to their needs and interests. KNOW YOUR AUDIENCE Define what you want the audience to do or understand. CLEAR OBJECTIVE Structure your presentation with a clear narrative. STORYTELLING
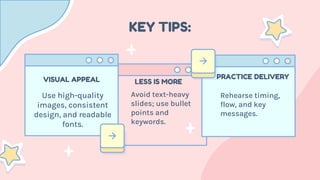
- 24. KEY TIPS: Use high-quality images, consistent design, and readable fonts. VISUAL APPEAL Avoid text-heavy slides; use bullet points and keywords. LESS IS MORE Rehearse timing, flow, and key messages. PRACTICE DELIVERY
- 25. KEY TIPS: Ask questions, encourage interaction, use visuals effectively. ENGAGE THE AUDIENCE Hook the audience early and leave a lasting impression. STRONG OPENING & CLOSING Stick to your alloted time. TIME MANAGEMENT
- 27. WHAT IS HYPERLINK? - A hyperlink (or simply “link”) is a reference to data that the user can directly follow either by clicking, tapping, or hovering. It points to a whole document. In presentations, it allows presenters to jump to other slides, external websites, or files.
- 28. I. FUNCTIONS AND PROCESSES OF HYPERLINK Navigation – Jumping to specific slides within the same presentation (internal links). External Resources – Linking to websites, online videos, or external documents (external links) File Access – Opening other files stored on your computer or network. E-mail – Initiating an email message. Process – Select text or an object, right-click (or use Insert tab), choose “Hyperlink”, and specify the link destination (existing file/web page, place in this document, create new document, email address).
- 30. EMBEDDING FILES AND DATA: DEFINITION – Embedding means inserting an object (like a document, spreadsheet, video, or audio file) directly into a presentation file, making it part of the presentation itself. Unlike linking, the embedded object does not rely on the original source file being present or accessible. PURPOSE – Ensures that the content is always available within the presentation, even if the original source file is moved or deleted. It makes the presentation self-contained. EXAMPLES - Embedding an Excel chart, a Word document, a PDF, or a video file directly into a PowerPoint slide. CONSIDERATIONS – Embedding increases the file size of the presentation.
- 31. This comprehensive outline covers the essential elements for mastering advanced presentation skills, from understanding the tools to crafting effective messages and utilizing advanced features like hyperlinks and embedded content.
- 32. ANY QUESTIONS?
- 33. 1. What is Presentation Tool? 2-5. Give atleast 4 Presentation Tools Application. 6-10. What are the Functions and Processes of Hyperlink? QUIZ TIMEEE!!!