7theroaringtwenties-150502091354-conversion-gate01.pptx
- 2. The Twenties • America would enter a new age of prosperity with automobiles, telephones, and electricity making life better. • American’s began focusing on making more money and enjoying themselves. • The 20s would be a period of economic prosperity and of new cultural values. • But, it didn’t start that way!
- 3. The Post War Recession • After World War 1, America went into a period of isolationism, refusing to be drawn into Europe’s drama. • Government stopped spending money on the war effort. • Factories shut down to convert to making civilian products. • Soldiers returned home from war and had a hard time finding work. • Farmers lost money since their European market was gone.
- 4. The Red Scare • The end of World War 1 brought new fears to Americans about Communists, anarchists, and immigrants. • In 1917, the Russians led by Lenin had a revolution, but instead of setting up a democracy, it became a communist nation. • Communists threatened to spread their revolution to other nations in Europe. • When labor strikes hit the USA in 1919 many in the USA feared a communist revolution happening in the U.S.
- 5. The Palmer Raids: •1919, Italian anarchist sets off bomb at Attorney General Palmers’s house. •It was one of series of attacks across America on that day. •The nation demanded action be taken. •The US Attorney General rounded up suspected communists, without warrants, and had them jailed or deported, often without any evidence of wrongdoing. The Red Scare This new fear of communism led the government to violate many individuals civil rights.
- 6. The Red Scare Sacco and Vanzetti: • - Two Italian immigrants who admitted to being communist were tried, convicted, and executed of a robbery & murder on flimsy evidence. • - Many thought they were executed for being anarchists and communists. This new fear of communism led the government to violate many individuals civil rights.
- 7. • The Red Scare, radical anarchist bombings, and the Sacco & Vanzetti trial led to a rise in nativism – the dislike of foreigners. • Nativists believed white Protestant Americans were superior to others. • These nativist attitudes would bring restrictions on immigration. • In the early 1900s over 70% of immigrants to the USA were from Eastern and Southern Europe, the ‘New Immigrant’ Rise of Nativism
- 8. • After World War 1, immigration was reduced to a trickle as nativists pushed for Congress to restrict European immigration for the first time. • The ‘New Immigrant’ without skills, education, or ability to speak English was seen as a threat to USA’s economic stability. • These ‘New Immigrants’ settled in the cities and added to the strain of providing public services. Rise of Nativism
- 9. Immigration Acts of 1921, 1924, and 1929 • These were laws designed to keep immigrants from Eastern and Southern Europe out of America. • Quotas were set allowing a certain number of immigrants from each nation to enter the USA. • Great Britain, Ireland, & Germany were allowed the most, while the ‘New Immigrant’ was limited, and the Asians were totally stopped. Rise of Nativism
- 10. Eugenics • During the 1920s there was a belief in the superiority of the Anglo-Saxon ‘race’. • The theory of Eugenics was the belief that the human race could be improved by breeding. • Many held racist beliefs that light-skinned, blond- haired, blue-eyed people were superior. • Social Darwinism was the idea that the different races competed for survival just like plants and animals did, this explained that the rich were rich because they were superior or better adapt.
- 11. Three Republican Presidents: Harding, Coolidge, & Hoover During the 1920s, three Republicans would control the White House for twelve years. They supported a laissez-faire policy of minimal government interference in business activities. Warren Harding Herbert Hoover Calvin Coolidge
- 12. Pres. Warren G. Harding • In 1920, Warren Harding won the presidency in a landslide. • Pres. Harding captured the national spirit with his campaign slogan of ‘return to normalcy’. • Harding focused less on foreign policy and more on peace and prosperity at home. • Under Harding the USA refused to join the League of Nations, lowered taxes, and restricted immigration.
- 13. Pres. Warren G. Harding • Pres. Harding urged tolerance towards other races, supported greater rights for African Americans, like anti- lynching laws and tolerance of Jews. • Pres. Harding appointed friends – the Ohio Gang - to positions of power. • The Teapot Dome Scandal was one of the worst in history, as one of Harding’s Cabinet members leased government land to friends for bribes. • Additional scandals included Harding appointees stealing money.
- 14. Pres. Calvin Coolidge • Calvin Coolidge served as Pres. Harding’s Vice Pres., when Harding died Coolidge became President. • Coolidge was re-elected again in 1924 on a pro-business policy and the slogan “Keep Cool With Coolidge”. • “Silent Cal’ had a motto of: “the business of America is business.” • The U.S. economy boomed under Coolidge, in fact some say that his laissez-faire attitude towards the economy led to over speculation that resulted in the stock market crash.
- 15. Pres. Herbert Hoover • Herbert Hoover organized U.S. food production in WW 1 and predicted the end of poverty if elected president. • Hoover was impressed with the achievement of business in raising the standard of living in America. • Hoover said this ‘rugged individualism’ had happened because: – Individuals were given equal opportunities, – They had a free education, – They had a will to succeed • Hoover felt too much government interference in business would ruin a good thing.
- 16. • Laissez-faire Economics • Rise of the Automobile • Other New Industries • More Efficient Production Techniques • Age of Mass Consumption Factors Responsible for the Prosperity of the 1920s
- 17. The Rise of the Automobile • The single most important factor behind the prosperity of the 1920s was the expanded use of the automobile. • Cars greatly affected all aspects of American life, as ownership rose from 8 to 24 million owners. • By 1929 1 out of every 9 jobs was in an auto-related business. • It also stimulated other industries like oil, steel, glass, & rubber.
- 18. • Cars gave people mobility. • Families went on vacations or to visit relatives. • People moved out of inner cities to the suburbs. • School buses allowed rural student to attend school regularly for the first time. • Rural people were no longer as isolated. The Rise of the Automobile
- 19. Henry Ford • Henry Ford didn’t invent the car, but he did perfect a way to make them cheaper and faster so more people could afford a car. • Ford pioneered the use of the assembly line to mass produce cars. • By 1924 Ford was producing one car every 10 seconds at a price of $300 per car. • He increased workers wages so they could afford to buy a car and other goods being mass produced
- 20. Rise of Other New Industries • The 1920s saw new discoveries and inventions in almost every field, opening the way for many new businesses. • Inventions made improvements in transmitting electricity to homes, businesses, & factories. • New household appliances like vacuum cleaners, refrigerators, toasters, coffee makers, stoves, radios, and motion pictures made life easier and more fun.
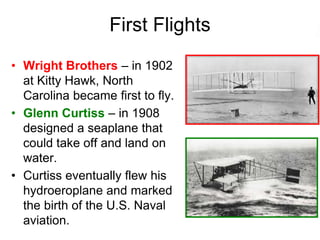
- 21. First Flights • Wright Brothers – in 1902 at Kitty Hawk, North Carolina became first to fly. • Glenn Curtiss – in 1908 designed a seaplane that could take off and land on water. • Curtiss eventually flew his hydroeroplane and marked the birth of the U.S. Naval aviation.
- 22. More Efficient Production Techniques • New manufacturing techniques, such as the assembly line, led to improved efficiency. • As efficiency increased consumers benefitted from lower prices for goods. • An unintended consequences of this improved efficiency was that skilled workers were no longer needed leading to an increase in unemployment.
- 23. The Age of Mass Consumption • Production techniques changed and so did patterns of consumption. • Goods began to be mass marketed on a national level. • Advertising stimulated demand. • Workers were receiving higher wages and they had more money to spend and also more leisure time. • The more money a person made the more things thing’s they wanted to buy.
- 24. • Consumers for the first time began buying on credit. • VISA, MasterCard, and other credit cards were not yet around, but installment plans were easy for a person to pay a small down payment and take the item home and then pay a little each month. • Suddenly Americans were in debt! The Age of Mass Consumption
- 25. Speculation Boom • Speculation is the purchase of an item, not for personal use, but in the hope of selling it later at a higher price, to make a quick n’ easy profit! • 1920s saw millions speculate in the stock market and in real estate (buying property). • The price of a share of a corporation skyrocketed as more and more people began to invest in the stock market.
- 26. Uneven Prosperity • But not everyone shared in the prosperity of the 1920s. • A small percentage of Americans had the largest percent of the wealth. • With new farm equipment, electricity & fertilizers farmers faced lower incomes due to overproduction of crops. • Textile workers faced competition for jobs with immigrants. • Minority Groups faced discrimination.
- 27. Temperance Movement and Prohibition • During the Progressive Era the growth of Temperance Movement (those against the drinking of alcohol) led to the passage of 18th Amendment. • The Temperance Movement thought that drinking alcohol was sinful, led to crime, and domestic violence. • Frances Willard was an outspoken leader of Temperance Movement, women’s rights, women’s suffrage & better working conditions for labor.
- 28. Prohibition - 18th Amendment • In 1919, the U.S. Congress passed the 18th Amendment to the Constitution which banned the manufacture, sale, or distribution of alcohol. • But instead of people obeying the law there was a growing disrespect for the law. • Speakeasies and bootlegging alcohol allowed the average consumer to obtain liquor without any problems.
- 29. Prohibition - 18th Amendment • Many Americans believed that Prohibition tried to force one group’s morals on others. • Still others opposed Prohibition because it closed breweries, bars, and distilleries where thousands worked. • Many said that Prohibition led to an increase in organized crime, the gangsters which willingly supplied illegal booze to consumers became rich and famous.
- 30. • By 1933, the American public saw that Prohibition was a ‘failed experiment’. • People had been unwilling to accept the law, Pres. Harding even served alcohol in the White House. • The 21st Amendment repealed or did away with Prohibition. • Prohibition proved that unpopular laws are often unenforceable. Prohibition - 18th Amendment
- 31. The Bible vs. Science Fundamentalism vs. Modernism The Scopes Monkey Trial In the 1920s many southern states passed laws making it illegal to teach Darwin’s Theory of Evolution in schools. John Scopes taught evolution in his Tennessee Biology class and was arrested and put on trial for it. The Scopes Monkey Trial became the most sensational trial of the decade.
- 32. • William Jennings Bryan prosecuted John Scopes and Clarence Darrow defended him. • The Scopes Trial was the first trial to be broadcast over radio, as it pitted older religious beliefs against newer scientific theories, • Darrow cross-examined Bryan about inconsistencies in the Bible and made him look old school and out of touch with the modern world. • The result of the trial was that Scopes was found guilty and fined $1. The Scopes Monkey Trial Man did not come from a monkey You haven’t seen my cousin
- 33. The Emergence of New Values Traditional values that had existed in America before the 1920s were found to be old and outdated. Instead the 1920s led to newer, more modern values which encouraged a greater openness and self-expression. Changes in music, art, literature, and sexuality provided the opportunity for expression of these freedoms.
- 34. Changing Roles of Women • Women had demonstrated their abilities during World War I. • A booming economy created new jobs & more women began working outside the home. • Women wanted equality with men in all areas. • In 1920, the 19th Amendment gave women suffrage or the right to vote. These women worked for women’s suffrage
- 35. • A new independent attitude began to appear among young, urban women. • These new women came to be known as flappers. • These flappers took more risks, cut their hair short, wore short skirts, smoked and drank in public, danced, and even chewed gum. Changing Roles of Women Flappers came to symbolize the new freedoms that many women felt during the 1920s • Women of today owe a great deal to the flappers who helped women gain their independent spirit!
- 36. STAAR Practice – Question # 1 • Using the images answer the question below. Which image shows the changing roles of women as women began to experiment with new found freedoms during the 1920s? Image A Image B Answer Image B Image A Image B
- 37. Tin Pan Alley • Following the Civil War, thousands of pianos were sold, as a result the sale of sheet music exploded. • Around 1910, New York City became the music publishing capital. • Tin Pan Alley, a section of New York, was the center of this activity. • Song-writing and musical ideas mixed together to form American popular music.
- 38. • Publisher found that average people bought sheet music for popular tunes, just so they could play this music at home. • Vaudeville became the most popular form of entertainment and its shows had a great need for music. • Musicians like, Scott Joplin, Irving Berlin, Cole Porter, and George Gershwin became famous. Tin Pan Alley Click Image
- 39. Youth and the Lost Generation • During the 1920s, young adults were responsible for zany fads, like flagpole sitting and marathon dancing. • Dances like the Charleston became wildly popular. • New words came into use: – Bootlegging – hiding booze in your boot or pant leg. – Speakeasies – place to buy illegal booze. – Flat Tire – dull, or boring person – Gam – a girl’s leg – Jake – okay – Spifflicated - drunk – White Cow – a vanilla milkshake
- 40. • A new group of writers, known as the “Lost Generation”, rejected the desire for material wealth. • These writers believed they did not fit the patterns of everyday life after the horrors of World War I. • The Lost Generation felt America had become overly materialistic and lacked spirituality. Youth and the Lost Generation Ernest Hemingway Wrote about W.W. I experiences in ‘A Farewell to Arms’ Sinclair Lewis Ridiculed the narrowness and hypocrisy of American life in ‘Main Street’ F. Scott Fitzgerald About rich, but unhappy man in ‘Great Gatsby’
- 41. The Great Migration • During the 1920s many African Americans began moving out of the South to the ‘Promised Land’ of the Northern cities. • This mass movement became known as the Great Migration. • They left in search of jobs in the industrial cities, and to escape sharecropping, tenant farming, and the deep racism of the South. • It changed the culture of these northern cities, especially Harlem, a section of New York.
- 42. The Harlem Renaissance • The 1920s is often called the Jazz Age, because of the importance of the new form of African American music. • This ‘rebirth’ in the interest of the African American culture became known as the “Harlem Renaissance”. • The Renaissance was more than just about the music, it included dance, visual arts, literature, and poetry. Cab Calloway at the Cotton Club
- 43. The Harlem Renaissance • Langston Hughes – writer/poet who expressed his pride in his heritage as well as attacking racism. • Countee Cullen – won more major literary awards than any other African American writer. • Zora Neale Hurston – one of first successful African American women writers, her greatest novel “Their Eyes Watching God”
- 44. Back-to-Africa Movement • Marcus Garvey was a controversial political activist know for his fiery speeches and his fancy uniforms. • Garvey formed the ‘Universal Negro Improvement League’ with a goal of total liberation of African people around the world. • There was disillusionment with those who had ‘migrated’ to the North. • The frustration of coping with urban life and the racism that had followed many African Americans set the stage for his Back-to-Africa Movement.
- 45. Popular New Heroes • The 1920s saw people have more leisure time and a greater opportunity for entertainment. • The American public embraced spectator sports, the radio, movies, and magazines. • On the radio people tuned into hear drama, crime, or mystery stories. • Charlie Chaplin was one of the early movie stars. Charlie Chaplin movie It happened in the 1920s
- 46. Charles Lindbergh • In the 1920s a $25,000 reward was offered to the 1st person to fly across the Atlantic Ocean to deliver the mail. • On May 20, 1927, Charles Lindbergh became the first person to fly solo across the Atlantic. • Lindbergh’s flight made him a national hero and he opened the way for commercial flights between America and Europe!
- 47. Popular New Heroes Babe Ruth and Jack Dempsey Sports figures became legendary heroes during the 1920s, Click on Black Screen to see Babe Ruth Click on Black Screen to see Jack Dempsey
- 48. Summary of the Roaring 20s The 1920s was a time of great excitement and rapid changes that ended with a crash! The 1920s started out slowly but grew into a period of great prosperity. A fear of communism, immigrants, & alcohol helped create feelings of mistrust, hatred, and unlawfulness. Women’s suffrage, flappers, Ford cars, the Harlem Renaissance, and new technologies made the 1920s an exciting time to live. The 20s roared until the stock market crashed and brought on the Great Depression.