An Introduction To Model View Controller In XPages
- 1. It’s Just A View An Introduction To Model View Controller In XPages Ulrich Krause, BCC GmbH Ghent, Belgium, March 30-31, 2015
- 2. • Administrator /Developer since 1993 • Senior Software Architect at BCC, Germany • OpenNTF Contributor • IBM Champion (2011 – 2015) • Blog http://www.eknori.de • Twitter @eknori • Mail ulrich.krause@eknori.de About: Ulrich Krause
- 3. • The constant in live and software development • Software Quality / Maintenance • Design Patterns • The Basics of MVC • Example Agenda
- 4. • The only constant in live is CHANGE Heraclitus (520 - 460 BC)
- 5. • The only constant in software development is CHANGE Heraclitus (520 - 460 BC)
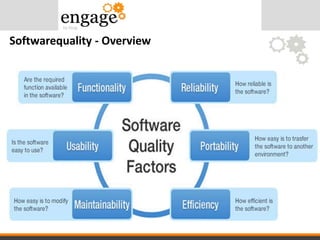
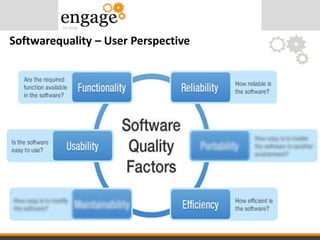
- 7. Softwarequality – User Perspective
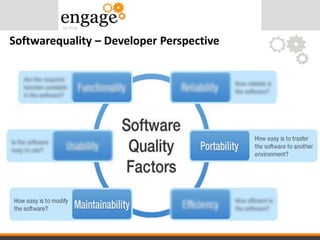
- 8. Softwarequality – Developer Perspective
- 9. • Challenges with „historically grown“ applications – Code can be everywhere in the application • Forms, View Events, Buttons, Hotspots, Script Libraries … – Use of different languages • LotusScript, @Formula, Javascript, Java, Simple Actions, HTML … – Redundancies • One possible solution is to seperate the Frontend from the Backend Code. – NotesDocument – NotesUIDocument Software Quality / Maintenance
- 10. Design Patterns
- 11. • Recurring solutions to software design problems you find again and again in real-world application development. • A general reusable solution to a commonly occurring problem in software design. • It is a description or template for how to solve a problem that can be used in many different situations. • Are about design and interaction of objects, as well as providing a communication platform concerning elegant, reusable solutions to commonly encountered programming challenges. • GoF Patterns are considered the foundation of all design patterns. What are Design Patterns?
- 12. • A design pattern is not a finished design that can be transformed directly into source or machine code • A design pattern is not a code snippet that can be copied into your code. Design Patterns are NOT
- 13. • Ralph Johnson, Erich Gamma, Richard Helm, John Vlissides Gang Of Four - GoF
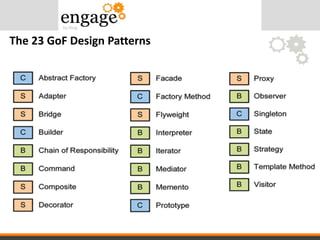
- 14. The 23 GoF Design Patterns
- 15. • MVC was one of the first works to describe and implement software constructs in terms of their responsibilities. • Trygve Reenskaug introduced MVC in the 1970s • In the 1980s, Jim Althoff and others implemented a version of MVC . • MVC was expressed as a general concept, in a 1988 article. Brief History Of MVC
- 16. • Trygve Mikkjel Heyerdahl Reenskaug (born 1930) is a Norwegian computer scientist and professor emeritus of the University of Oslo. • He formulated the model-view- controller (MVC) pattern for Graphic User Interface (GUI) software design in 1979 while visiting the Xerox Palo Alto Research Center (PARC). Father Of MVC http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trygve_Reenskaug
- 17. • You created a superhero web application/website for a comic shop owner with a small database table. • it is a huge success and your client is extremely satisfied. • They ask you to change the application, they want to use a different database and, according to market demand, they definitely need both iPhone and Android apps. • Now repeat this five times. • The client keeps on asking for modifications and expansions. • These can be UI related changes and even complete backend architecture . Why MVC? – An Example Project Case
- 18. It‘s Official, We‘re In Deep Doo-Doo Now …
- 19. • … you’d notice that some things would have been less painful • And you’d been happier However if you used MVC from the start
- 20. • 90% of the code for the web application and the mobile app will be the same, but instead of saving the user data to a Shared Object or through a web service, you’d be using a local DB for instance. • Without MVC, chances are pretty high you’ll be making modifications in a bunch of classes. • The same applies to the UI for instance. Only the way it’s presented to the user is different. Why ?
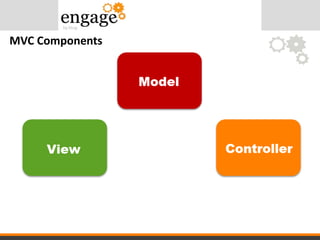
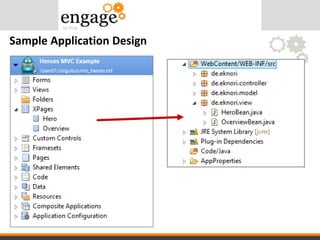
- 21. MVC Components
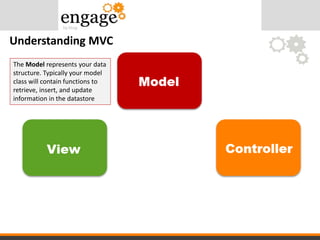
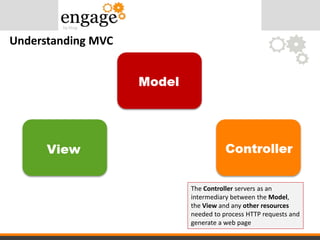
- 22. Understanding MVC The Model represents your data structure. Typically your model class will contain functions to retrieve, insert, and update information in the datastore
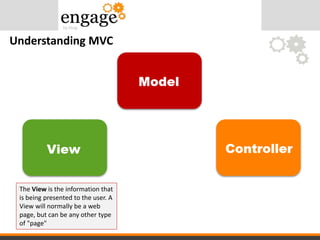
- 23. Understanding MVC The View is the information that is being presented to the user. A View will normally be a web page, but can be any other type of "page"
- 24. Understanding MVC The Controller servers as an intermediary between the Model, the View and any other resources needed to process HTTP requests and generate a web page
- 25. • The Model is the data, • The View is the window on the screen, • And the Controller is the glue between the two An easy way to understand MVC
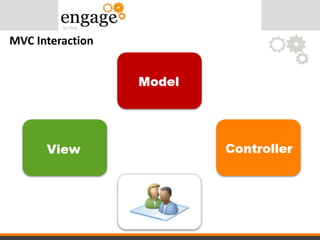
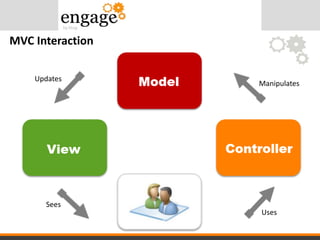
- 26. MVC Interaction
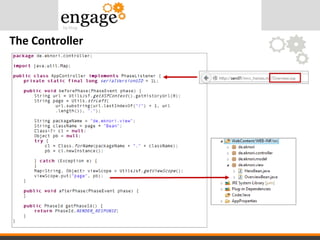
- 33. The Controller
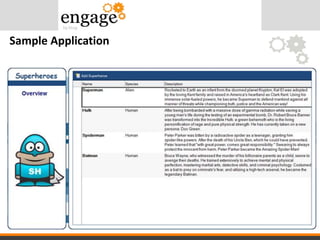
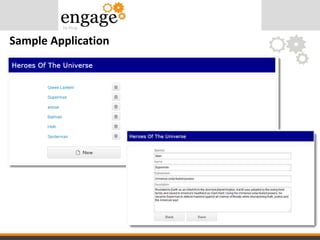
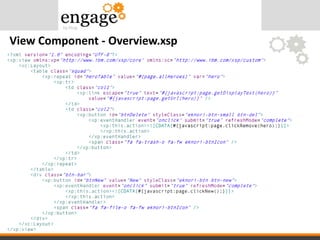
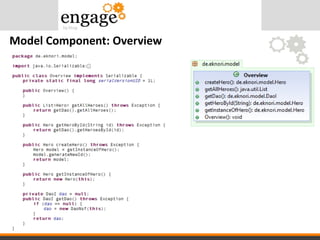
- 34. View Component - Overview.xsp
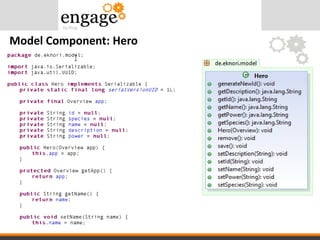
- 35. View Component - Hero.xsp
- 38. • A data access object (DAO) is an object that provides an abstract interface to some type of database or other persistence mechanism. • All read / write data operations are delegated to DAO. • No other part of the application has direct access to the underlying datastore Data Access Object ( DAO )
- 39. Changes - What Management Wants …
- 40. Changes - What You Think …
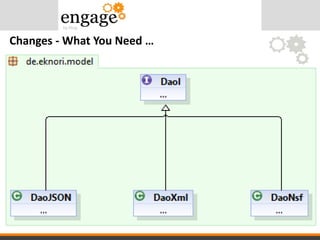
- 41. Changes - What You Need …
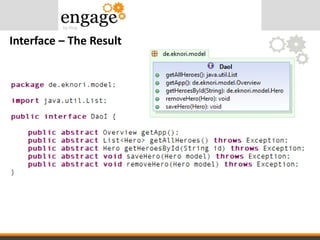
- 42. • An interface in the Java programming language is an abstract type that is used to specify an interface (in the generic sense of the term) that classes must implement. • Interfaces are declared using the interface keyword, and may only contain method signature and constant declarations (variable declarations that are declared to be both static and final). Interface - Definition
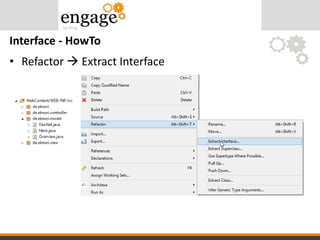
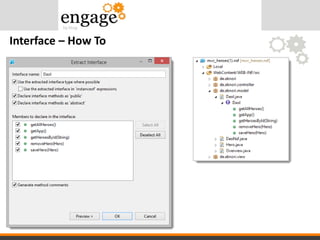
- 43. • Refactor Extract Interface Interface - HowTo
- 44. Interface – How To
- 45. Interface – The Result
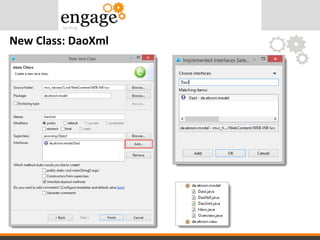
- 47. • Stubs for all methods and properties • ToDo: Write code to work with XML instead of NSF New Class: DaoXml
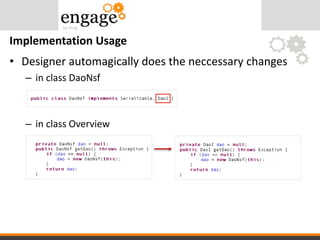
- 48. • Designer automagically does the neccessary changes – in class DaoNsf – in class Overview Implementation Usage
- 49. • Depending on which datasource to use, change that one line in your code. And Finally …
- 51. • Architexa helps you to understand and to document large/complex codebases. • Design Patterns in Java Tutorial • Gang Of Four Useful Links
- 52. Q & A Twitter @eknori Mail ulrich.krause@eknori.de
- 55. Software Quality – Use The Right Tools
Editor's Notes
- #11: Software Design Patterns are about reusable designs, interaction of objects and high quality solution to a given requirement, task or recurring problem. So Design Patterns are documented, tried and tested solutions or recurring problems in a give context. They are reliable and they speed up software development process.
- #12: Let’s 1st talk about software design patterns. Software design patterns can be defined as recurring solutions to common problems in software design. You might be wondering how does your application work without design patterns if this’s so important. The main point to understand is that if your application doesn’t contain any errors it will work like a charm. But working application does not mean that your application’s codebase is up to the industry standard. Just writing code is not gonna help you but writing the code right way will help you. GOF A.K.A. Gang Of Four(Erich Gamma, Richard Helm, Ralph Johnson and John Vlissides) are considered to be the gurus of software design patterns. They introduced 23 design patterns which fall into three types. Creational design patterns, Structural design patterns and behavioural design patterns. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Software_design_pattern
- #13: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Software_design_pattern
- #14: 1970-s: "A Pattern Language" , by C. Alexander, et al. , 1977 (available at amazon.com) 1980-s: Hillside Group - Beck, Ward, Coplien, Booch, Kerth, Johnson, etc. 1995 - the famous book - "Design Patterns: Elements of Reusable Object Oriented Software", 1995, by the so-called Gang of Four (GoF), that is Erich Gamma, Richard Helm, Ralph Johnson and John Vlissides - see their photo:
- #16: https://www.lri.fr/~mbl/ENS/FONDIHM/2013/papers/Krasner-JOOP88.pdf The MVC pattern has subsequently evolved,[13] giving rise to variants such as HMVC, MVA, MVP, MVVM, and others that adapted MVC to different contexts
- #22: An easy way to understand MVC: the model is the data, the view is the window on the screen, and the controller is the glue between the two A model is an object representing data or even activity, e.g. a database table or even some plant-floor production-machine process. A view is some form of visualization of the state of the model. A controller offers facilities to change the state of the model Controller The Controller in the MVC comes at the last, but is the most used part of the MVC pattern. It is used to work with the HTTP requests, coming from the clients; from the browsers or from any other application that can generate an HttpRequest (not to be confused with the .NET’s HttpRequest object; but a simple HTTP Request). Each request, when comes, is handled by the Controller and then Controller, according to the request makes decisions to load the data, create the response and then sends the data back to the client. It should also be noted here, that your Controller acts as a bridge between your Model and the View. Because they, as themself, cannot perform any action. Controller triggers their events and makes them do something, like return data from Model, or to render the HTML document from the View etc. All of the resources and errors are also handled by the Controller. Making it the heart of the pattern, because the response is also sent back from a controller. You can think of an example of a Controller to be the entire Business-logic-layer. The code that is used to run the application’s back-end processing, like creating accounts, managing solutions etc, would make up the Controller section of this pattern. View Next comes the part of the View, this is the actual web page that is being displayed to the user. It contains the HTML codes that are to be sent back to the data as a response to his request. Correct, Controller sends this response back to the client, View – its self – doesn’t send this response to client whereas Controllers takes this data, and sends back to the client. View, can also be created dynamically. As already said, all of the requests are handled by Controller, so any parameter (including QueryStrings) can also be handled by Controllers. Using these parameters, we can generate dynamic Views. So dynamic content in our view, change their layouts or show some other error messages if the data sent is not of our own choice. View, generally depends on the Model that is being used to create the View and these dynamic data objects are capture from the Model (Model is discussed in the next section). Point to be noted here is that while section-in-action is View, still Controller is playing a vital role for passing the values and for retrieving the data to be sent to client. Model As the name suggests, it is a model of some object. The object in this case is our application’s data. It can be of any type, like extracted from a database; no matter which one, SQL Server, MySQL or MS Access etc, or it can be a simple data that comes from a Reporting, or from a Spreadsheet etc. Model is never shown to the user (actually, the client) because he is supposed to see the data and the results we want him to see, that is why, it is a good approach to keep a great abstraction layer between Model and the user (the client). Model doesn’t only store the data, it – at the same time – keeps the View and the Controller updated or any change being made to it. Models are designed, just like Controllers and Views are designed, just so that there is no ambiguity between three of them and it is easy for them to communicate to make the web application fluent. Everytime a change is made, View is update by the Controller, because Controller is informed about the change (this informing event is also raised by Controller; as I already said, Controller handles the events). To store anything in the Model, the user has not been provided with any form that is directly connected to the Model, instead a form is generated in the View by the Controller for the user to fill in. Once the form is filled, the form values are then passed to the model for storing purposes. All kinds of data validations (most special type of which are SQL Injections) can be checked at the Controller level rather than loosing (important) data.
- #33: Every XPages has a corresponding Java class Hero -> HeroBean, Overview -> OverviewBean
- #34: When the user submits the URL, in the BEFORE phase event the Appcontroller gets the page name from the url. It first splits the URL to get the last part -> Overview.xsp, then again, it splits the result to just get the name -> Overview From the VIEW package, it gets the class OverviewBean, creates a new instance and stores the object in the viewScope.
- #35: There is no classic data binding. The repeat control accesses the viewScope. The viewScope is manipulated by the AppController. „page“ contains the bean object for the page.
- #39: The Data Access Object Pattern, also known as the DAO pattern, abstracts the retrieval of data from a data resource such as a database. The concept is to "separate a data resource's client interface from its data access mechanism." The problem with accessing data directly is that the source of the data can change. Consider, for example, that your application is deployed in an environment that accesses an Oracle database. Then it is subsequently deployed to an environment that uses Microsoft SQL Server. If your application uses stored procedures and database-specific code (such as generating a number sequence), how do you handle that in your application? You have two options: Rewrite your application to use SQL Server instead of Oracle (or add conditional code to handle the differences), or Create a layer inbetween your application logic and the data access The Data Access Object pattern does the latter. The benefits of the DAO pattern are obvious, but the implementation is a little tricky. To properly implement the DAO pattern you need to generate the following components: DAO Interface DAO Factory DAO Implementation classes Deployment Descriptor Entry The DAO pattern, in and of itself, does not necessarily require a factory, but in practice you will see the two patterns coupled. The reason is that some mechanism needs to be created to obtain the appropriate implementation class and using a factory is the cleanest implementation http://www.informit.com/guides/content.aspx?g=java&seqNum=137 http://www.tutorialspoint.com/design_pattern/data_access_object_pattern.htm